Jump to the section
- Key Learnings
- What are Gamification and Serious Games?
- Key Differences Between Gamification and Serious Games
- Serious Games in Project Management
- Types of Serious Games Used in Project Management
- Key Areas Covered by Project Management Serious Games
- Gamification in Project Management
- Gamification Elements in Project Management
- Agile Gamification Examples
- Project Management is a Serious Game
- FAQs
Key Learnings
#1
Linking Theory and Practice
Serious games and gamification close the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world project management challenges. Serious Games provide a hands-on approach in risk-free environment.
#2
Enhance Engagement and Motivation
Learn how gamification elements like points, badges, and leaderboards transform routine tasks into exciting challenges. Keep your team motivated, collaborative, and focused on project goals.
#3
Develop Your Critical Skills
Understand how serious games cultivate both technical and soft skills, such as like leadership, decision-making, and communication. They are essential for managing complex projects effectively.
#4
Adopting Innovative Tools
Learn how integrating serious games and gamification into project management can revolutionize education and training. You adopt powerfull tools for learning and storytelling for training your project team.
Imagine a project where timelines go out of control, motivation dries up, and objectives are delayed further away. A familiar story for most of the project managers. Mastering project management in a volatile business environment is not about knowing frameworks and methodologies, it is about applying them well under pressure and changing conditions.
To overcome such project challenges, project managers need practical experience. This means handling the real world, not only theoretical techniques. No classroom or workshop can cover such a practical gap. But how to gain this practical experience without putting projects at risk?

Serious games and gamification for project management can cover this gap between practical experience and education (Rumeser et al.). Serious games are essentially interactive, immersive experiences in a simulated environment that simulates real-life project scenarios. They offer a safe place to try out strategies and develop your decision-making skills. You can make mistakes without any significant risk to the organization. On the other hand, gamification will borrow the elements of game design to translate into your daily tasks, turning routine project management activities into engaging challenges.
These approaches are not only about making learning fun, but they are transforming how project managers close the gap between theory and practice. Serious games and gamification engage project teams to provide a dynamic platform for confidence building, improved collaboration, and tackling complexity head-on.
In this article, we’ll explore how serious games and gamification are reshaping project management, offering leaders and teams new ways to thrive in an ever-changing landscape.

🎮 Serious Games & Gamification: Transforming Project Management! 🚀
What are Gamification and Serious Games?
What is Gamification?
Gamification is defined as the application of game design elements and mechanics in non-game contexts to motivate users to increase engagement. It makes the ordinary, extraordinary by adding points, badges, leaderboards, and rewards. The whole process transforms simple tasks into interactive and rewarding experiences that encourage active participation and achievement.

Gamification History
Although gamification became mainstream in 2010, its roots go back to 2002. In time, it has developed into one of the most prominent tools used in various industries. By 2011, it had already proven its potential to drive engagement across a wide range of fields, from education to commerce. This growth proves how well it can make normal, mundane tasks more engaging and effective.
Core Mechanics of Gamification
The core of gamification is its game elements. Progress bars visually display the indicators of achievements, and levels show mastery and motivate users to want more. Challenges and storytelling are an immersive narrative that keeps users connected with their goals. Combined, gamification creates a structured and engaging experience.
Gamification in Education
Used in education, gamification is a technique to increase learners’ motivation and engagement. It may be through awarding points for completing assignments, creating leaderboards to encourage friendly competition, or issuing badges to recognize achievement in milestones. All these tools make learning more enjoyable, interactive, and effective at transforming traditional tasks into rewarding experiences.
The Complexity of Gamification
While gamification often increases engagement, its success depends on thoughtful design. To be sure, it cannot be a one-size-fits-all approach, for it is crucial to understand what drives users and then calibrate the game mechanics around their needs. Poorly designed or implemented systems may never yield the results they hope to achieve; hence, careful planning is absolutely important.
The Versatility of Gamification
Gamification is not confined to education. Examples can be found in many industries. Loyalty programs in commerce reward repeat customers with points for creating brand loyalty. Fitness apps encourage users by tracking steps and offering badges for goals reached. Many government and healthcare systems use gamification to increase user engagement and, in that way, improve outcomes. Its applications make it a useful tool in every context.
What are Serious Games?
Serious games are games that are designed for a purpose other than pure entertainment. They are different from the normal traditional games that are made for fun only because they are designed with a leading primary purpose and used in real-world challenges within an artificial environment. They are specifically made to keep people engaged while achieving the intended educational or professional goals.

Purpose of Serious Games
Serious games are designed to target specific learning objectives. This provides a structured platform for the participant to engage deeply in knowledge transfer, development of new skills, and change in behavior. Such games, therefore, bring great value to industries where traditional ways are failing or proving less effective in mapping complexity and motivating participants.
The Versatility of Serious Games
One of the strongest points of serious games is their versatility. They are applied in the most diverse possible fields, starting with healthcare, education, and corporate training. Besides, they do not reside only in the digital space; nondigital forms, like board games or interactive workshops, can impact learning equally well. With this flexibility comes the idea that serious games are customized to specific audiences or contexts.
Principles of Technology and Design
At their core, serious games utilize game technology and design principles to create a purposeful learning environment. To keep the participants engaged and drive home key concepts, they incorporate elements such as challenges, narrative, and rewards. Their design is deliberate and combines entertainment with certain learning outcomes.
Simulated Environments for Experiential Learning
Serious games are good at creating a simulated environment in which participants can learn through experience. These simulations mimic real-life situations, allowing users to experiment, make decisions, and observe the consequences of those actions. This experiential learning closes the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, enabling learners to build confidence and develop critical thinking skills.
Constructivism and Practical Experience
It has been noted that constructivist learning—that is, learning in which knowledge is built by the occurrence of experience and not simply passive absorption—takes place in a big way through serious games, involving participants actively to eventually construct practical experience, better retaining what’s on hand. Engaging learners with a process will result in lessons that will truly stick.
Key Differences Between Gamification and Serious Games
The great difference between serious games and gamification lies in the design and purpose of these two concepts. Serious games are full-fledged games designed for purposes other than pure entertainment, such as education, training, or behavioral change. These are immersive games—full, self-contained experiences designed to engage participants deeply and achieve targeted learning goals.
Gamification involves adding game elements such as points, badges, leaderboards, and progress bars to non-game activities. Rather than creating stand-alone experiences, gamification enhances existing processes to motivate users and increase engagement. As an example, project management software might incorporate gamified features to encourage task completion or improve team collaboration.
Both, in a sense, use game mechanics, but the real difference lies in how and for what they are applied. Serious games are standalone learning products, while gamification adds elements of games to other activities to make them more fun. They both offer relatively unique ways of improving learning and reaching goals in widely varying environments.
| Aspect | Serious Games | Gamification |
| Definition | Complete games designed for a purpose beyond entertainment, such as learning or training. | The use of game elements like points, badges, and leaderboards in non-game settings. |
| Purpose | Focuses on achieving specific learning objectives or skill development. | Aims to motivate users, enhance engagement, and encourage participation. |
| Design | Self-contained, immersive environments with standalone gameplay. | Enhances existing activities or processes by adding game-like features. |
| Examples | Simulations for project management, leadership training, or healthcare scenarios. | Gamified project management software, and fitness apps with rewards for goals. |
| User Experience | Offers a fully immersive experience tailored to learning or practicing skills. | Creates engagement by integrating gamified features into everyday tasks. |
| Learning Focus | Provides hands-on, experiential learning in simulated environments. | Focuses on improving user behavior and task completion. |
| Implementation | Requires comprehensive design and development as standalone tools. | Easier to implement by layering game elements onto existing systems. |
Serious Games in Project Management
Serious games provide a completely different approach to project management education and training. They make the traditional approach dynamic and interactive. In project management, serious games offer professionals real-life situations to exercise their skills in a virtual environment. They offer learners the chance to engage actively, think critically, and exercise strategies in a controlled setting.
The most significant benefit of serious games is the ability to provide experiential learning. Unlike passive learning methods, serious games put participants into simulated project situations where they can make decisions and see the results in an instant. That kind of hands-on approach improves not just understanding but also confidence in the techniques being applied to a real-world scenario.
These project management games target skills development, where participants get the chance to improve both their hard and soft skills. While working in a team, solving conflicts, and managing resources correctly, essential abilities such as communication, leadership, and decision-making are developed. This makes them a very strong tool in the hands of a project manager seeking to develop his or her professional skills.
Another great advantage is that it’s a risk-free environment. Learners can try different strategies, review their consequences, and learn from mistakes made without the pressure of real-world consequences. That will promote creativity, seeking new challenges, and trying new methods.
Moreover, serious games increase participants’ engagement and motivation. These kinds of activities, because of interactivity and competitiveness, create a positive learning environment that keeps students engaged and motivated to perform better.

Types of Serious Games Used in Project Management
Serious games come in a variety of forms, each with its unique way of improving project management education and training. Closing the gap between theory and practice, these games give learners ample opportunity to experiment, develop skills, and be immersed in experiences tailor-made for the challenges of the real world.
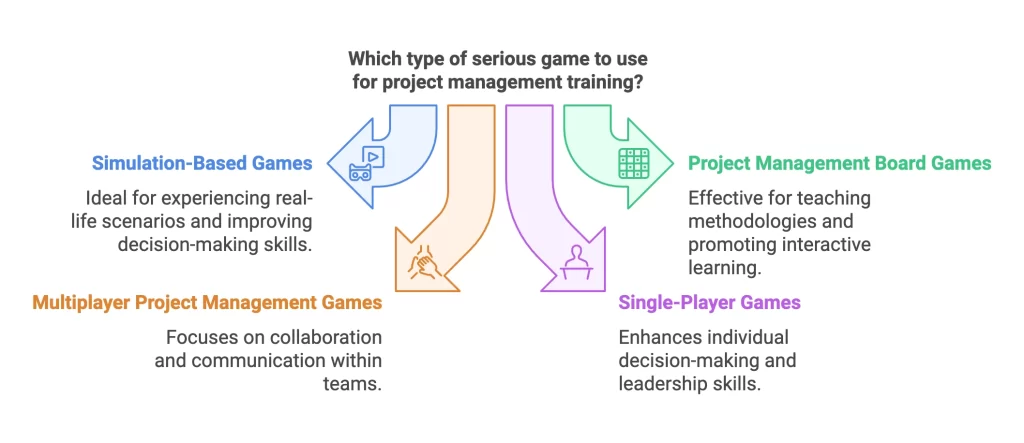
Simulation-Based Games
Simulation-based games are among the most commonly used types in project management. These games simulate real-life situations in which participants are placed in the role of a project manager. Using simulations, learners experience issues of resource allocation, stakeholder communication, and risk management in a safe and controlled environment. These experiences can improve decision-making and critical thinking. This is helping build confidence for real-life applications.
Project Management Board Games
Agile and Waterfall methodologies can be taught effectively with the aid of project management board games. They use physical game components to teach concepts such as team collaboration, adherence to timelines, and planning of resources. These non-digital games allow interactive learning and make complex concepts more accessible and engaging for players.
Multiplayer Project Management Games
Multiplayer project management games emphasize collaboration and communication. They simulate team dynamics, showing players how to collaborate with others, manage conflicts, and make group decisions. These games show very well how shared goals and different perspectives can bring success to a project.
Single-Player Games
Single-player games emphasize individual decision-making skills. They are designed to improve personal accountability, problem-solving, and leadership. The players, through the working of the project scenarios alone, come to know their strengths and areas of improvement that can be translated into enhanced performance in their respective jobs.
Project Management Serious Games Examples
One example is The Project Win Game, where one plays out the difference between traditional/waterfall and agile approaches to project management. Other simulations recreate various project scenarios so learners may attempt different strategies. In an interesting contrast, while the student respondents preferred the games as a result of humor, aesthetics, and their group nature, simulation exercises were preferred in terms of clarity and accessibility.
Key Areas Covered by Project Management Serious Games
Project management serious games are designed to provide a comprehensive view of key project management areas. This can support the ability to navigate multiple project scenarios. Aligned with established frameworks like PMI PMBOK knowledge areas, these games deliver a robust learning experience that prepares participants for the challenges of realistic projects.
One of the strengths of serious games is their focus on critical knowledge areas, such as time management, cost management, risk management, and procurement management, that are foundational to effective project management and are often included in-game scenarios. The participants get hands-on experience applying these principles by working through simulated realistic challenges.
From initiation through closing, serious games cover the project life cycle in addition to knowledge areas. That holism ensures that the learner will be furnished with the ability to manage projects from start to finish and fosters an appreciation for how different stages interconnect.
Serious games also lend themselves to various industries. They include simulation of projects in the fields of engineering, construction, IT, and general management. With the increasing usage of agile methodologies, many games now incorporate elements from Scrum and Kanban methodologies. This enables exploration in the agile management of projects through gaming. This versatility shows that serious games keep their promise in a dynamically changing world.
Beyond the technical skills, recent trends put greater emphasis on “soft” skills: communication, collaboration, and stakeholder engagement. The answer to modern demand in project management lies increasingly with these topics. Of course, integration, time, and cost management are well covered, but there’s so much more room for growth in areas like communication, procurement, and quality management.
With such a wide scope of coverage, project management games help professionals develop both technical expertise and interpersonal skills, which are indispensable in leading different types of projects to success.
Gamification in Project Management
Better Stakeholder Engagement
Gamification of project management uses game mechanics and elements, such as points, badges, or leaderboards, throughout project processes. The use of these techniques will make routine tasks more dynamic and inspire teams to be motivated toward delivery. Gamification transforms work into a structured, yet fun, challenge aimed at fostering collaboration and productivity.
Among the most important advantages of gamification is better stakeholder engagement. Project stakeholders can actively participate in the project life cycle through game elements such as leaderboards or progress tracking. When stakeholders see their efforts recognized and ranked, they start feeling more connected to the success of a project.
Motivating Project Teams
Gamification is a very powerful tool for keeping the motivation of a project team high. Tracking progress, rewards over milestones can be achieved. Collaboration through challenges makes the team more accountable and strengthens teamwork. In the gamification of agile project management, gamified sprints, and task boards encourage alignment while making sure that everyone is focused on their goals.
The Role of Game Mechanics and Elements
Gamification uses the mechanics of points, badges, leaderboards, and rewards to engage participants. Gamification makes projects more exciting by turning task completion into a competitive and rewarding experience. Having clear goals and immediate feedback, gamification keeps teams energized and results-oriented.
Learning Through Mistakes
One of the biggest advantages of gamification is the secure learning environment. Mistakes will become opportunities to improve one’s strategies without real-life consequences. The process increases reflection, which in return improves decision-making and develops confidence.
Promote Collaboration and Communication
Gamification often leads to teamwork, healthy competition, and effective communication. These benefits create a positive workplace culture and enhance collaboration. This is important for the successful execution of objectives in projects.
Gamification Application
Many organizations use project management gamification to motivate employees and align them with company goals. For example, gamified project tools with leaderboards or sprint rewards encourage employees to be motivated. This is making management processes more efficient and enjoyable.
Gamification Elements in Project Management
Gamification in project management uses various elements and techniques for project team and stakeholder engagement. These elements focus on providing an engaging experience and tracking progress, actions, and behaviors. The following are the more widely used gamification elements in project management.
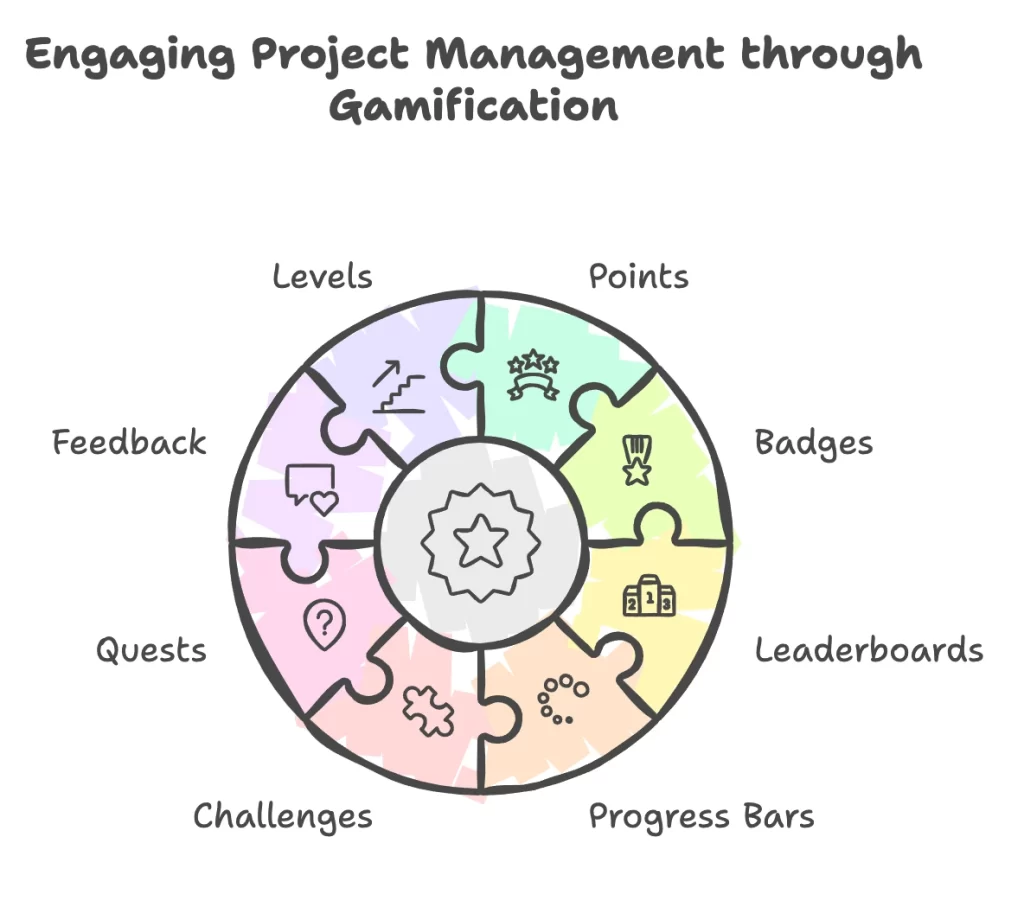
Points for Driving Progress
Points awarding used to complete tasks. This creates a sense of progress tracking. Points provide a quantifiable reward for effort, allowing team members to visualize their achievements and stay motivated. This simple and powerful element instigates consistent task completion and reinforces dedication to the project’s goals.
Badges for Celebrating Milestones
Badges are a visual celebration of success. They are given to team members when they reach milestones. They symbolize recognition and accomplishment while building pride and motivating individuals to strive for more. Whether it’s for completing a sprint or hitting a major deadline, badges are an ongoing source of encouragement.
Leaderboards for Inspiring Performance
Leaderboards create healthy competition by ranking individual members of a team or group based on their contributions. This gamification of tracking performance not only identifies top performers but also encourages others to do better. Leaderboards further enhance accountability. This is a signal that productivity is a challenge taken on by the whole team.
Progress Bars for Visualizing Success
A progress bar brings instant clarity to task completion. By breaking them down into smaller, visual steps, complex projects are kept focused and on track using progress bars. They provide immediate feedback that ensures everyone understands how their efforts contribute to the bigger picture.
Challenges for Increasing Engagement
Bringing challenges into the workflow of a project injects an element of problem-solving and interaction. These tasks will push teams to think creatively and work collaboratively, making the routine more dynamic and rewarding. Challenges raise engagement among the members and spark innovative solutions.
Quests for Guiding Exploration
Quests add a narrative layer to gamification. They walk participants through structured steps, helping to break big objectives into smaller, bite-sized tasks. The sense of purpose and discovery that quests provide is engaging for team members as they explore different areas in a project.
Feedback for Focusing on Growth
Direct feedback in gamification is important. Real-time guidance and recognition make the team members feel supported by showing them their progress. Such feedback reinforces learning because the teams adjust strategies for more wins.
Levels for Progressive Growth
Levels symbolize growth in expertise. Showing accomplishment, and striding up through levels, team members feel a sense of growing within a particular role, progressing further because of what they are. This is what keeps motivation alive, moving individuals to seek mastery and contribution on higher levels.
Storytelling for Creating Connection
The use of storytelling within the projects brings about a feeling of connection and immersion. The compelling narrative brings the project to life, where every team member starts to see their roles as part of a larger, meaningful story. Such emotional engagement increases their focus and commitment.
Agile Gamification Examples
Agile gamification uses the game elements and mechanics in agile practices. This develops a more engaging and motivational environment for agile teams. Pointing systems, badges, and leaderboards make them collaborate, perform better, and make agile workflows way more immersive and funny experience.

Stories Points for a Sense of Accomplishment
Allocating points for the user stories and sprint tasks is engaging. This encourages team members to be more productive and focused on tasks. Adding badges for reaching milestones, such as the completion of a complex user story or sprints, creates a strong sense of progress and accomplishment.
Team Challenges for Driving Sprint Velocity
Making routine tasks into collaborative competitions with challenges will increase sprint velocity. For example, teams can compete on resolving the most user stories or completing high-priority tasks. Such challenges not only drive productivity but also build teamwork. This keeps teams energized and aligned to the agile project objectives.
Leaderboards at the Agile Boards
Leaderboards show top contributors in agile teams across boards. This fosters friendly competition and transparency among team members. The recognition of top performers motivates not only the individual but also the whole team to improve collectively. Transparent tracking of contributions increases accountability and keeps everybody striving for excellence.
Sprint Retrospectives for Feedback Loops
Sprint retrospectives can be gamified. This can make ordinary reviews interactive. This allows point awards for actionable feedback or creative solutions keeps the team members engaged and ensures meaningful discussions. This strengthens communication and fosters a mindset of continuous improvement.
Project Management is a Serious Game
Serious games and gamification aim to change the face of project management education and training. Combining innovation with practical application, these tools provide dynamic, hands-on experiences that will prepare individuals for the navigation of complex, real-world projects. Invaluable in building technical and soft skills, they have proven quite capable of simulating scenarios in a no-risk environment, including decision-making, leadership, and communication.
Serious games are appreciated for their ability to concretize the abstract into an actionable based on tangible insights. Immersive learning supports experimentation and safe failure, then refines strategies accordingly. On the other hand, gamification uses motivation and engagement to drive the performance of the team and also nurtures a sense of achievement. These two approaches combine and bring kinetic dynamism into learning where more traditional methods may sometimes fail.
However, success demands thoughtfully holistic implementation. Serious games and gamification should support organizational objectives and be one component of a well-crafted learning architecture. Leaders and educators able to adopt serious games and gamification benefits will be able to create tailor-made, high-impact learning experiences for their teams.
FAQs
Serious games are immersive simulations designed for educational or professional purposes. They allow project managers to practice decision-making, leadership, and communication skills in a risk-free environment, bridging the gap between theory and real-world application.
Gamification uses game elements like points, badges, and leaderboards to make routine project management tasks engaging and motivational. It fosters team collaboration, tracks progress, and promotes accountability.
Serious games are standalone learning tools designed for specific purposes, such as training or education. Gamification, however, involves adding game mechanics to non-game contexts to enhance engagement and motivation in existing processes.
Serious games help develop both technical skills (like time and risk management) and soft skills (such as leadership, communication, and collaboration) in simulated project scenarios.
Agile gamification incorporates game mechanics like points, badges, and leaderboards into sprints and agile workflows. It enhances team engagement, improves sprint velocity, and creates interactive retrospectives for continuous improvement.
