Jump to the section
Key Learnings
#1
Enbrace Modern Leadership Styles
Discover how transformational, coaching, and empowering leadership can effectively engage Gen Z by fostering autonomy, mentorship, and collaboration.
#2
Build an Inclusive Workplace
Learn the importance of diversity and inclusion, and how to create safe online environments that support and retain Gen Z talent.
#3
Promote Continuous Growth
Understand how to provide ongoing learning opportunities and regular feedback to motivate Gen Z and enhance their professional development.
#4
Leverage Technology and Flexibility
Explore strategies for integrating digital tools and offering flexible work arrangements to meet Gen Z’s expectations and boost productivity.
Generation Z represents the generation born between the mid-1990s and early 2010s [Hidayat et al., 2023]. It is rewriting the rules of the workforce with their unique characteristics and preferences. As the first true digital natives, Gen Z grew up surrounded by technology and the Internet. [Yılmaz et al., 2024] This instilled in them a preference for a collaborative workplace as tech-savvy. Gen Z’s comfort with digital platforms makes them global citizens in their own right, using technology to drive innovation and seamless communication.

Our article gives you insights and strategies for leading Gen Z people. The research describes their preference for empathetic leadership, which values authenticity, respect, and purpose-driven work. Understanding these preferences is key to motivating and keeping them working productively [Baldonado et al., 2018].
Leading Generation Z at work requires adaptability on the part of the leaders since traditional ways of leadership largely prove inadequate. Gen Z requires new approaches that will conform to their unique behavior and needs [Zehetner-Hirtenlehner, 2023], [Dwidienawati et al., 2023].
The modern workplace is filled with Baby Boomers, Generation X, Millennials, and now Gen Z. Each generation has its unique qualities; however, the entry of Gen Z into the workforce is a major change. Their diversity, combined with their digital fluency, is rewriting workplace dynamics [Jayatissa, 2023].
Projections show that Gen Z will soon make up a large portion of the global workforce, and they are the leaders of the future. Added to their status as the most diverse generation, this underlines the need for leaders to adopt tailored strategies to integrate and engage them effectively [Lazar et al., 2023].

👩💻 Leading Generation Z: Strategies to Engage the Workforce of Tomorrow 🚀
What is Generation Z?
Generation Z (abbreviated as Gen Z), is generally defined by most researchers as birth years ranging from the mid-1990s to the early 2010s [Hidayat et al., 2023] [Hathaway et al., 2022].

Generations are shaped by the events and conditions of their lifetime years. Gen Z is not an exception. Among the prominent influences are the great 2008 Economic Recession and COVID-19. These major events affected dramatically the values and behavior of Gen Z. Those collective experiences have played a key role in forming their practical, financially cautious outlook with special emphasis on stability [Suarez and McKee, 2018].
Known as “digital natives,” Gen Z grew up with smartphones, social media, and a constant connection to the internet [Yılmaz et al., 2024]. Unlike previous generations, they have never been in a world without these technologies. Consequently, they are at ease with digital tools and platforms in almost all personal and professional life areas.
Sometimes they are called iGen or Post-Millennials [Maloni et al., 2019]. Generation Z is the most racially and ethnically diverse generation. They are highly educated and achievement-oriented with a higher college attendance rate than their predecessors. Gen Z is pragmatic and focused on security, valuing meaningful work and chances for advancement in their chosen workplaces [Singh et al., 2014].
Gen Z Key Characteristics
Entrepreneurial Spirit and Self-Reliance
Gen Z is entrepreneurial in spirit. They strive well in an environment where they can take initiative and contribute innovative ideas. Their adaptability and independence allow them to succeed in self-directed projects, where they can show off their skills in a unique way. Gen Z greatly appreciates autonomy and is not afraid of challenges [Baldonado et al., 2018]. Therefore taking ownership of work creates new paths towards success.
Authenticity and Commitment to Social Justice
Authenticity is one of the defining characteristics of Gen Z. They like engaging with organizations that show sincerity, modesty, and share their values. Social justice and environmental sustainability are high on their radar, so they seek employers who work with diversity, equity, and inclusion in mind. Companies taking action against societal and environmental challenges are the ones that will find a strong connection with this generation [Jayatissa, 2023].
Pragmatism, Diversity, and Social Consciousness
A pragmatic and fiscally cautious generation, Gen Z focuses on job security but still has the drive for ambitiousness and is goal-oriented [Suarez and McKee, 2018]. Most racially and ethnically diverse generation reflects a wide array of perspectives and priorities, which Gen Zers bring meaning to, hence they would want to contribute meaningfully in their workplace and community [Bodunde, W., et al., 2024].
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
Gen Z highly values flexible work arrangements, like remote or hybrid jobs. While some studies show that Millennials are more concerned with work-life balance, Gen Z’s emphasis on efficiency and mental health makes flexibility one of the main keys to their productivity and engagement [Forbes, 2023].
Gen Z Key Statistics
By 2030, Gen Z is expected to make up about 30% of the workforce, and every entry-level job in the US will be filled by a Gen Z [Gabrielova et al., 2021].
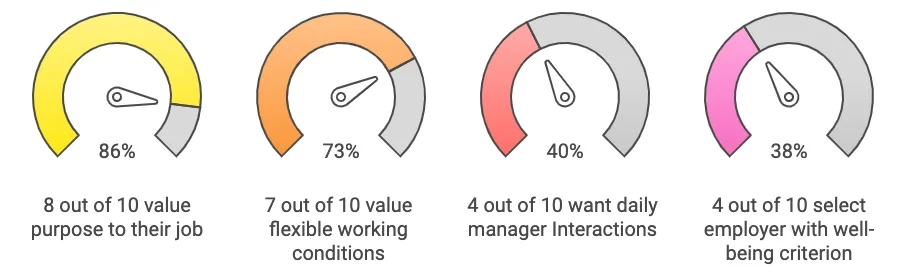
Purpose and flexibility are the definitions for what drives Generation Z at work, with key statistics [Mann K., 2023], [Gabrielova et al., 2021]:
- 86% of them seek a purposeful job critical to their well-being and satisfaction
- 73% seek flexible conditions in the form of remote or hybrid jobs
- 40% want daily interactions with their manager
- 38% say that well-being is one of the top factors in choosing an employer
Gen Z is the most achievement-oriented of the generations. They are the most racially and ethnically diverse generation, bringing an inclusive mindset to workplaces and expecting nothing less from employers regarding their equity and representation values [Schroth et al., 2019].
Gen Z vs. Other Generations
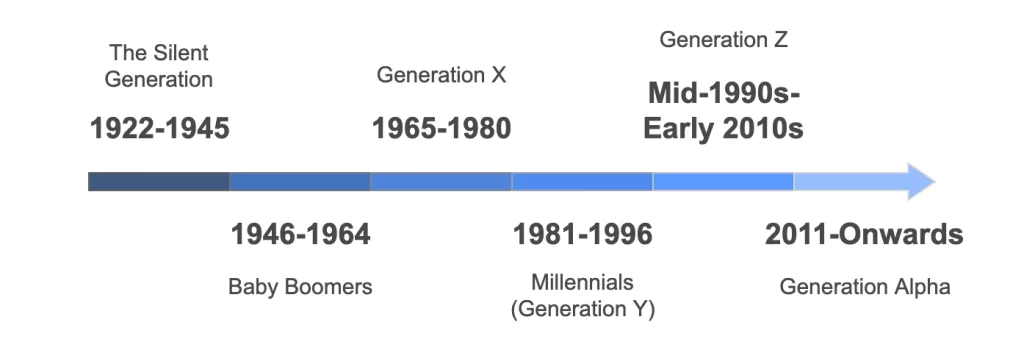
Baby Boomers vs. Gen Z
Baby Boomers are built on strong work ethic, teamwork, and job stability. They would emphasize flexible work arrangements less than Generation Z, for whom flexibility is one of the primary engagement and productivity factors [Gabrielova et al., 2021].
Generation X vs. Gen Z
Generation X, having grown up with face-to-face interactions during their formative years, values independence and work-life balance. Unlike Generation Z, they are less immersed in technology and more reliant on traditional communication styles. Gen X prefers stability but cautiously adopts new work trends; hence, they often act as a bridge between Baby Boomers and younger generations [Hidayat et al., 2023].
Millennials (Gen Y) vs. Gen Z
While both Millennials and Gen Z want purpose-driven work, the priorities of each generation are different. Millennials care more about work-life balance and prefer collaborative work environments, while Gen Z values flexibility, the ability to work from anywhere, and independence. They are high achievers and sometimes impatient to achieve quick accomplishments, whereas Gen Z is practical and less entitled. Millennials are established in their careers, usually in management, while Gen Z is just starting recently their careers [Baldonado et al., 2018], [Gabrielova et al., 2021].
Generation Z vs Generation Alpha
The emerging Generation Alpha is expected to be even more immersed in technology than Gen Z. Generational differences, such as perceived narcissism, are often linked to youth rather than cultural values, which also implores leaders to approach these generations with nuance [RUIZ VÁZQUEZ, M.H., et al., 2024].
| Generation | Values | Work Style | Technology Use | Flexibility |
| Baby Boomers | Job stability, teamwork | Traditional, structured | Minimal reliance | Low |
| Generation X | Independence, balance | Independent, in-person | Gradual adoption | Moderate |
| Millennials | Collaboration, goal-setting | Team-oriented, proactive | Comfortable with tech | Moderate-High |
| Generation Z | Pragmatism, purpose | Independent, adaptable | Digital natives | High |
| Generation Alpha | Tech immersion, adaptability | Emerging | Highly integrated | High |
Leadership Styles for Gen Z
Why Leadership Styles Are Important
Effective leadership styles’ foundation is what directs how teams work, innovate, and succeed. Leaders inspire tasks and attitudes, creating an environment where productivity and satisfaction thrive. For Gen Z, leadership has to click with their values: autonomy, purpose, and inclusion. Organizations can develop strategies to motivate and retain Gen Z workers by understanding these preferences, which drives organizational success [Baldonado et al., 2018], [Dwidienawati et al., 2023].
The right leadership style can completely change the dynamics at work. Inspiring leaders, through whom the team gets a boost in performance and further engages in their respective jobs, is vital. Workplace satisfaction among Gen Z is satisfied by supportive leadership, encouraging participation in decision-making, just conflict resolution, and rewards for contribution on an individual level. All align with what Gen Z wants when considering meaning and purpose in life [RUIZ VÁZQUEZ, M.H., et al., 2024].
Salaries are not enough to keep Generation Z engaged. Leaders need to offer growth possibilities, ownership of tasks, and a sense of belonging. Organizations that invest in fitting their leadership approach to the needs of Gen Z will develop resilient teams and decrease turnover. As Gen Z becomes a dominant workforce demographic, leaders must adopt these changes to stay competitive and future-ready [Kulkarni and Rai, 2023].
Essential Leadership Characteristics for Gen Z
Gen Z requires a balance of clarity, empathy, flexibility, and technological savviness. With these key characteristics, you can earn trust and speak to this generation’s values and expectations.
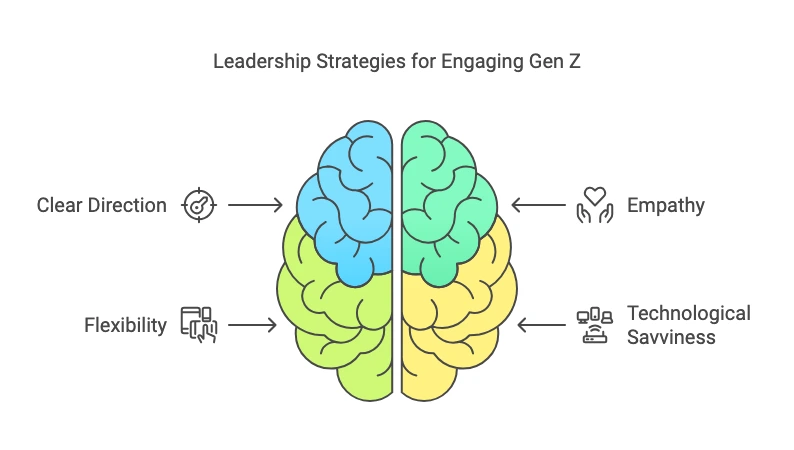
Clear Direction and Ongoing Feedback
Generation Z does well with clear structure and expectations. Leaders can lead Gen Z by establishing clear goals, giving regular feedback, and providing growth opportunities. Regular check-ins, progress tracking, and frequent action advice can lead to high engagement. Gen Z focuses on stability and wants to ensure that their contributions impact the organization. This instills their confidence and purpose in their work. Clear communication of corporate values and career pathways continues to inspire Gen Z, keeping them engaged and motivated, and in line with the organizational mission [Dwidienawati et al., 2023], [Forbes, 2023].
Empathy and support.
Leaders who are good listeners, validate concerns, and provide personalized support make Gen Z employees feel loyal and perform well. Addressing the specific challenges of Gen Z consequently calls for engaging on a deeper level: mentorship, being easily accessible, and showing genuine concern for the welfare of employees make leaders both more relatable to and respectable in their eyes. These traits will, therefore, be used to fuel commitment from Gen Z and increase job satisfaction [Kulkarni and Rai, 2023], [Yılmaz et al., 2024].
Flexibility and Tech-Savviness.
Gen Z insists on flexibility, such as providing remote work options, flexible time schedules, and fulfillment of personal needs, to achieve a better balance of work and life. Leaders who use technology wisely, using digital tools for communication, training, and collaboration, create a workplace that Gen Zers like. Keeping up with technological trends assures smooth interaction and engagement [Zehetner-Hirtenlehner, 2023], [Kwartawaty et al., 2024].
Which Leadership Styles does Gen Z prefer?
Understanding Gen Z’s leadership styles is very important for leading the next workforce generation. Gen Z seeks purpose, collaboration, and autonomy. Leaders whose styles adapt to Gen Z values can establish better connections with employees and higher engagement.

Transformational Leadership
Transformational leadership encourages the actualization of potential through a shared vision and personal development opportunities. This style will resonate with Gen Z’s need for meaningful work and clear career direction. Transformational leaders inspire trust and commitment by communicating a compelling vision, demonstrating enthusiasm, and promoting innovation. They establish clear goals, offer professional development opportunities, and challenge team members to strive for excellence. Research shows such leadership style boosts performance, satisfaction, and commitment in Gen Z [Dwidienawati et al., 2023], [Kwartawaty et al., 2024].
Coaching Leadership
Coaching leadership focuses on mentorship and skill development, focusing on Gen Z’s need for ongoing feedback. Leaders who provide individualized support and guidance help Gen Z employees grow and succeed. Practical applications include offering regular feedback, creating learning opportunities, and assisting employees in setting and achieving goals [Brown, 2023], [Hathaway et al., 2022].
Servant Leadership
Servant leadership is about empathy and team welfare. Gen Z respects leaders who listen actively, nurture their development, and build a team-oriented work environment. Activities like teamwork, sensitively dealing with challenges, and concern for the welfare of employees build trust and loyalty [Dwidienawati et al., 2023], [Lim and Lianto, 2024].
Empowering Leadership
Empowering leadership builds autonomy by delegating authority and trusting employees to make decisions. Gen Z values the independence this style offers and the opportunity to grow their confidence and skills. Leaders can demonstrate this style by recognizing accomplishments, delegating responsibilities, and providing resources for development [Magano et al., 2020], [Zehetner et al., 2022].
Democratic leadership
Democratic leadership is about collaboration and inclusiveness, which Gen Z appreciates. What this generation values most are environments where their voices are heard and their ideas are respected. Leaders with this leadership style involve their team in decision-making, encourage open communication, and develop a culture of shared purpose [Yılmaz et al., 2024], [Zehetner et al., 2022].
Four Practical Strategies for Leading Gen Z
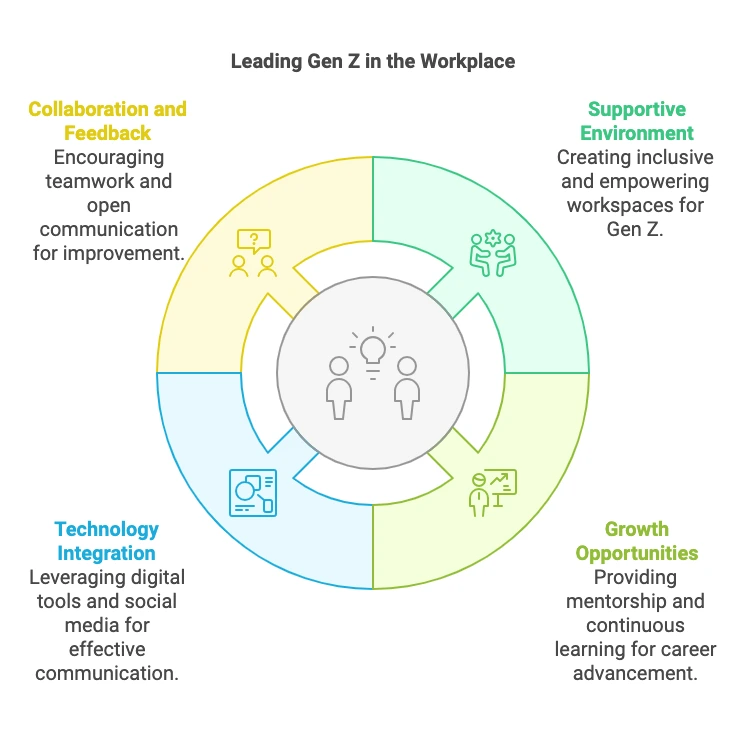
Strategy 1: Creating a Supportive Work Environment
To lead Gen Z effectively, leaders must start respecting their values and manage the expectations of this generation. Leaders must create a supportive, inclusive, and empowering work environment. This will allow them to learn how to motivate and lead Gen Z employees effectively.
Build Safe and Inclusive Online Spaces
As digital natives, Gen Z expects the workplace to integrate technology into the work environment seamlessly. Creating a safe and inclusive online space is important for comfort and productivity. Leaders can achieve this by setting clear guidelines for digital engagement, moderating online discussions, and preventing harassment. Also, they should use diverse communication tools that focus on the preferences of each individual. Psychological safety—feeling comfortable sharing ideas and expressing concerns—is foundational for collaboration and innovation [Hidayat et al., 2023], [Zehetner-Hirtenlehner, 2023].
Promoting Respectful Interactions and Addressing Cyberbullying
Respectful communication is important to keep the workplace healthy. Cyberbullying can be very detrimental to both mental health and performance. Leaders should role-model good behavior, train on online etiquette, and have zero-tolerance anti-bullying policies in place. Swift and decisive responses to incidents reported, coupled with extensive support systems, guarantee a culture of trust and safety [Schroth et al., 2019], [Singh et al., 2014].
Fostering Diversity and Open Communication
Gen Z is the most diverse generation and shares the values of inclusion and equity. Leaders can celebrate diversity by encouraging dialogue, addressing bias immediately, and ensuring that all voices are heard. They must establish open communication through multiple digital channels and build trust to ensure engagement [Hathaway et al., 2022].
Make them Feel Valued
Leaders must provide recognition and empowerment. Gen Z needs to celebrate achievements, have challenging but meaningful work, and be empowered to make decisions. Leaders must understand their drive for growth, purpose, and flexibility. All of these can create an environment where Gen Z feels valued and thrive [Schroth et al., 2019], [Singh et al., 2014].
Strategy 2: Providing Growth and Development Opportunities
Generation Z employees have a strong desire to grow, learn, and be able to put their skills on display. Leaders can motivate them through structured mentorship, experiential learning, continuous development, and meaningful recognition. Here’s how to motivate Gen Z employees to thrive.
Mentoring and Leadership Workshops
Mentorship is a critical component of Gen Z employees’ professional development. These provide Gen Z with personalized guidance and practical insights. It gives them also the confidence to overcome challenges in the workplace. Leadership workshops will empower Gen Z by developing key skills such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. Structured environments where they can practice leadership while networking with peers resonate strongly with their ambition to lead [Hidayat et al., 2023], [Baldonado et al., 2018].
Experiential Learning Opportunities
Gen Z learns better by doing. The best way for them to apply knowledge is through hands-on projects, internships, and interdisciplinary tasks that simulate real-world scenarios. Activities such as role-playing, job rotations, and youth-led initiatives develop emotional intelligence and critical thinking. Those opportunities provide not only practical experience but also the confidence to take ownership of their leadership journey [Maloni et al., 2019], [Magano et al., 2020].
Recognition and Continuous Learning
Acknowledgment and development go together with Gen Z. They respond to specific praise, public recognition, and increased responsibilities. Their development can be supported by giving them access to online courses, workshops, and certification programs. They need regular feedback and coaching on matching their current roles with long-term career aspirations to emphasize their value in the organization [Mann K., 2023], [Brown, 2023].
Strategy 3: Leveraging Technology and Communication
Cultivate in your team with Gen Z’s digital-first mindset. You need to integrate as much as possible technology into their workflows, use social media strategically, and foster interactive online communities.
Integrate Digital Tools
Digital tools are an important element of Gen Z’s way of working. Technology platforms allow for quick, accessible, and efficient communication. Digital memos, or knowledge sharing in teams, can include multimedia like videos and infographics. It is making them engaging and easy to consume. Online platforms for training offer great flexibility, as they can be used for self-paced learning. If designed properly, they can offer an immersive gamified experience. Leaders utilizing digital tools ensure their Gen Z teams remain informed and empowered [Hidayat et al., 2023], [Suarez and McKee, 2018], [Kulkarni and Rai, 2023].
Communicate more with Social Media
Social media are an important part of communication for Gen Z people. Leaders can use these platforms to acknowledge successes, share company news, and create a sense of community. Sharing individual stories and content that is authentic and humorous hits the right notes with Gen Z’s values. When employees see themselves reflected in the company culture through social media, their motivation and loyalty increase [Hathaway et al., 2022], [Forbes, 2023].
Building Engaging Online Spaces
Creating tech-savvy, interactive online spaces makes Gen Z feel connected and valued. Tools that enable collaboration, idea-sharing, and respectful interactions breed a sense of inclusion. Leaders can nurture a thriving virtual community by using creative approaches like interactive polls, shared project platforms, and moderated discussions. It enhances not just engagement but encourages ownership among employees [Hathaway et al., 2022].
Strategy 4: Fostering Collaboration and Feedback
Finally, you need to embrace collaboration, provide actionable feedback, and give autonomy. These strategies are in line with Gen Z values, fostering trust, innovation, and engagement.
Building a Collaborative Workplace
Gen Z values teamwork and a sense of community, even as they embrace independence. They do well in environments where there is openness in sharing ideas and learning from each other. Well-defined purpose and roles in team efforts strengthen their commitment and creativity. Even though Gen Z likes managing their projects, it’s through collaboration that they can put their skills into action, be innovative, and see the tangible outcomes of contributing meaningfully toward organizational goals [Zehetner-Hirtenlehner, 2023], [Arefiev et al., 2023].
Involving Gen Z in Decision-Making
Gen Z wants a voice and an appreciation for a decision-making process where opinions count. A sense of involvement in organizational decision-making enhances motivational levels, a sense of ownership, and loyalty in them. The leaders should first create an environment where they can voice their concerns, contribute to discussions, and understand the motives behind decisions to strengthen their linkage with the organization and fuel meaningful engagement [Kulkarni and Rai, 2023],[Schroth et al., 2019].
Regular and Constructive Feedback
Raised in a culture of social media with a short attention span and instant feedback. Therefore Gen Z expects regular and constructive feedback. Timely and honest feedback combined with recognition of achievements engages them. Regular personal feedback, rather than yearly reviews, ensures their growth and accountability [Baldonado et al., 2018], [Suarez and McKee, 2018].
Empowering Through Autonomy
Micromanagement will destroy Gen Z’s creativity and motivation. They work best in an environment where there is continuous guidance but independence in how tasks are executed. Only when they are trusted, given space to make decisions, and supported when needed will they thrive and stay engaged [Dwidienawati et al., 2023].
Leading the Future Leaders
Leading Generation Z at work is not only a challenge but also an opportunity to redefine the future of leadership. Gen Z brings fresh eyes and a perspective that emphasizes growth, authenticity, and purpose in professional lives. Transformational, coaching, and servant leadership are just a few of the leadership styles. They need trust, growth, and motivation. Each of these meets the needs of Gen Z in their quest for personal and professional growth, a sense of belonging, and doing something meaningful within their organizations.
Gen Z thrives under leaders who embrace empathy, humility, and adaptability. They appreciate the work environment where their voices are heard, their contributions recognized, and their autonomy respected. Open communication, continuous feedback, and clear guidance are critical in fostering trust and engagement. Allow them to better leverage technology, and social media and create inclusive online spaces. This enhances their work experience and makes connecting with and inspiring them easier.
Those organizations that understand and adapt to Gen Z’s differentiators will attract and retain talent. This is going to drive innovation and create long-term success in the future. Nurture the entrepreneurial spirit, adaptability, and social consciousness of Gen Z’ers—all forces for positive change. All this together means building relationships with them, communicating actively, and leading by example.
What are some of the strategies you feel work best with Gen Z? Let us know in the comments, and let’s keep talking about how to create leaders for tomorrow!
FAQs
Generation Z is entrepreneurial, self-reliant, and highly tech-savvy. They value authenticity, social justice, diversity, flexibility, and work-life balance. Additionally, they seek purposeful work, continuous growth opportunities, and environments that support their mental well-being.
Transformational, coaching, servant, empowering, and democratic leadership styles resonate best with Gen Z. These styles emphasize autonomy, mentorship, empathy, inclusiveness, and collaboration, aligning with Gen Z’s values and expectations.
Leaders can foster a supportive environment by promoting diversity and inclusion, leveraging technology effectively, ensuring respectful interactions, providing recognition, and creating safe online spaces. Encouraging open communication and addressing issues like cyberbullying promptly also contribute to a positive workplace.
Organizations should offer structured mentorship programs, experiential learning opportunities, leadership workshops, and continuous learning through online courses and certifications. Regular feedback and recognition of achievements also help in motivating Gen Z employees.
Technology is crucial for Gen Z as they are digital natives. Leaders should integrate digital tools for communication and collaboration, utilize social media for engagement, and create interactive online spaces. Embracing a digital-first mindset ensures that Gen Z remains informed, connected, and empowered.
References
- Hidayat, Debra et al. “Gen Z Digital Leadership through Social Media.” WIDYAKALA JOURNAL : JOURNAL OF PEMBANGUNAN JAYA UNIVERSITY (2023): n. Pag. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Gen-Z-Digital-Leadership-through-Social-Media-Hidayat-Tjandra/c36be53b932814f62e2e7a9ff383b3d87ccaa500#citing-papers
- Ardi, Ardi et al. “Leader Readiness in Facing the Challenges of a VUCA Business Environment: Case Study of Generation Z.” European Business & Management (2024): n. Pag. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Leader-Readiness-in-Facing-the-Challenges-of-a-VUCA-Ardi-Meilani/b2f82197dd5bce005674ee263b85b71918704c37
- Ajmain, Talhah. “Impacts and Effective Communication on Generation Z in Industrial Revolution 4.0 Era.” (2020). https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Impacts-and-Effective-Communication-on-Generation-Z-Ajmain/b572ab79bb14454d28cbd1ae62fc9e7c2f31319a
- Lim, Albert Theriono and Lianto Lianto. “Ethical Leadership in the Eyes of Gen Z: A Literature Review.” FIRM Journal of Management Studies (2024): n. Pag. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Ethical-Leadership-in-the-Eyes-of-Gen-Z%3A-A-Review-Lim-Lianto/5d29c20356dd0d02b6f030997a4b1209551b05ce
- Magano, José et al. “Generation Z: Fitting Project Management Soft Skills Competencies—A Mixed-Method Approach.” Education Sciences (2020): n. pag. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Generation-Z%3A-Fitting-Project-Management-Soft-Magano-Silva/c276a9f35c579b3ccbb70f383001b6ea4917a0d4
- Jayatissa, K. A. D. U.. “Generation Z – A New Lifeline: A Systematic Literature Review.” Sri Lanka Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities (2023): n. Pag. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Generation-Z-%E2%80%93-A-New-Lifeline%3A-A-Systematic-Review-Jayatissa/a7f87d5c410f0a24a67e3bcd2df8ed041f5220eb
- Kulkarni, Dr. Vijay and Prof. Nikita Rai. “Generation Z Talent Management In Organisations: An HR Perspective.” Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences (2023): n. Pag. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Generation-Z-Talent-Management-In-Organisations%3A-An-Kulkarni-Rai/ed39daa60a4ece71cda394814611260d6f75023a
- Lazar, Mihai-Alin et al. “The Emerging Generation Z Workforce in the Digital World: A Literature Review on Cooperation and Transformation.” Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Excellence 17 (2023): 1991 – 2001. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-Emerging-Generation-Z-Workforce-in-the-Digital-Lazar-Zbuchea/c6ea98eef4dd9af707cf49ffd66eaf49b74cc01e
- Yılmaz, Betül et al. “Digital natives of the labor market: Generation Z as future leaders and their perspectives on leadership.” Frontiers in Psychology 15 (2024): n. Pag. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Digital-natives-of-the-labor-market%3A-Generation-Z-Y%C4%B1lmaz-K%C4%B1sa%C3%A7tutan/589d62a2aa69a704959c7cec59ba306d54336cbb
- Zehetner-Hirtenlehner, Daniela. “Formation of leadership style of Generation Z.” Actual problems of innovative economy and law (2023): n. Pag. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Formation-of-leadership-style-of-Generation-Z-Zehetner-Hirtenlehner/f22ca12938cad4a2557e6c9f902921dc81e814ba
- Baldonado, Arthur M.. “Leadership and Gen Z: Motivating Gen Z Workers and Their Impact to the Future.” (2018). https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Leadership-and-Gen-Z%3A-Motivating-Gen-Z-Workers-and-Baldonado/ed12f76702ee4fafb9a7960d1a4596ffde598b7b
- Zehetner, Andreas et al. “Generation Z’s expectations of their leaders: A cross-cultural, multi-dimensional investigation of leadership styles.” European Conference on Management Leadership and Governance (2022): n. pag.https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Generation-Z’s-expectations-of-their-leaders%3A-A-of-Zehetner-Zehetner/e1b4d41f17e73db394c2dfb92d215a72923262e7
- Suarez, Cecilia Elizabeth and Valerie McKee. “Preparing to Work with Generation Z.” EDIS (2018): n. Pag. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Preparing-to-Work-with-Generation-Z-Suarez-McKee/e30af14bd2d10035a205a8dd5249bc82955913b9
- Dwidienawati, Diena et al. “Effective Leadership style for Generation Z.” Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management (2023): n. pag.https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Effective-Leadership-style-for-Generation-Z-Dwidienawati-Syahchari/9649e27eba8eb9c0152153f731a1d9324875fa6a
- Mosca, Joseph B. and Janeth F. Merkle. “Strategic Onboarding: Tailoring Gen Z Transition for Workplace Success.” Journal of Business Diversity (2024): n. pag.https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Strategic-Onboarding%3A-Tailoring-Gen-Z-Transition-Mosca-Merkle/9162954a0c2f5ba98c9be878cbcf6b331668eedd
- Alya Shafira Agustia et al. “LEADERSHIP STYLE FOR Z GENERATION.” (2021). https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/68mh9. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/LEADERSHIP-STYLE-FOR-Z-GENERATION-Agustia/0a208ebd8a6bc5627b9a794f59c3a9e737615d0f?utm_source=consensus
- Andreas Zehetner et al. “Generation Z’s expectations of their leaders: A cross-cultural, multi-dimensional investigation of leadership styles..” European Conference on Management Leadership and Governance (2022). https://doi.org/10.34190/ecmlg.18.1.891. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Generation-Z’s-expectations-of-their-leaders%3A-A-of-Zehetner-Zehetner/e1b4d41f17e73db394c2dfb92d215a72923262e7?utm_source=consensus
- Nihan Yavuz Aksakal et al. “Revealing the Leadership Characteristics of the Modern Age: Generation-Z Perspective.” International Journal of Organizational Leadership (2024). https://doi.org/10.33844/ijol.2024.60397. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Revealing-the-Leadership-Characteristics-of-the-Aksakal-Ulucan/a2537f3b8818e347b2e99e82b4951e891f546e0d?utm_source=consensus
- Nana Noviada Kwartawaty et al. “Most Effective Leadership Styles for Generation Z: A Review.” Formosa Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (2024). https://doi.org/10.55927/fjmr.v3i9.11009. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Most-Effective-Leadership-Styles-for-Generation-Z%3A-Kwartawaty-Ismail/a559fec508b299e311f50d175576e34554904864?utm_source=consensus
- D. Bateh et al. “Leadership from Millennials to Generation Z Transformed.” Journal of Advanced Management Science, 6 (2018): 11-14. https://doi.org/10.18178/joams.7.1.11-14. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Leadership-from-Millennials-to-Generation-Z-Bateh/3795b7828296144a660e826ef777572dcdd2184a?utm_source=consensus
- Karina Gabrielova et al. “Here comes Generation Z: Millennials as managers.” Business Horizons (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BUSHOR.2021.02.013. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Here-comes-Generation-Z%3A-Millennials-as-managers-Gabrielova-Buchko/082d2f1a720b60f4314d26d428bb7972693424e5?utm_source=consensus
- S. Arefiev et al. “Prospects of leadership style formation regarding Generation Z..” Ukrainian Journal of Applied Economics and Technology (2023). https://doi.org/10.36887/2415-8453-2023-3-19. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Prospects-of-leadership-style-formation-regarding-Arefiev-Nemashkalo/6daf427fe391a54c612c2f3f1177479666e8b55c?utm_source=consensus
- P. Klein et al. “Leadership Perspective on the New Generations (Generation Y and Generation Z).” International journal of business and social science, 9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.30845/IJBSS.V9N10P4. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Leadership-Perspective-on-the-New-Generations-Y-and-Klein/7abecf6e42ca6ae7e7bf8ef7af194716d5be1a61?utm_source=consensus
- Holly A. Schroth et al. “Are You Ready for Gen Z in the Workplace?.” California Management Review, 61 (2019): 18 – 5. https://doi.org/10.1177/0008125619841006. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Are-You-Ready-for-Gen-Z-in-the-Workplace-Schroth/f19b8eca6968a085ba020e7c27330a676f4232c4?utm_source=consensus
- Anjali Singh et al. “Challenges and Issues of Generation Z.” IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 16 (2014): 59-63. https://doi.org/10.9790/487X-16715963. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Challenges-and-Issues-of-Generation-Z-Singh/b10973a5c6d11f37542adc34455bb0c7fbcbbb9d?utm_source=consensus
- Jens Berger et al. “New World of Work: How the Value System of Generation Z Is Changing Leadership.” Communications of International Proceedings (2023). https://doi.org/10.5171/2023.4145823. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/New-World-of-Work%3A-How-the-Value-System-of-Z-Is-Berger/19cb8be556f9ccb79195922733cd273fad5bda23?utm_source=consensus
- M. Maloni et al. “Understanding the work values of Gen Z business students.” The International Journal of Management Education (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2019.100320. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Understanding-the-work-values-of-Gen-Z-business-Maloni-Hiatt/80e2d503c03183f21a0e3dcdac1952444da97aa1?utm_source=consensus
- Liz Hathaway et al. “Understanding and Engaging Generation Z.” ACSM’S Health & Fitness Journal (2022). https://doi.org/10.1249/fit.0000000000000774. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Understanding-and-Engaging-Generation-Z-Hathaway-O’Shields/056e122f96b5421d20d2152e9e075d3efbc9a9bf?utm_source=consensus
- M. Jake Aguas, Millennial and Generation Z’s Perspectives on Leadership Effectiveness, https://www.regent.edu/journal/emerging-leadership-journeys/gen-z-generation-z-leadership/
- Patrick Brown, Effective Leadership Styles for Engaging the Gen Z, https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/effective-leadership-styles-engaging-gen-z-workforce-patrick-brown/
- Kiran Mann, Guiding The Next Generation: Understanding And Leading Gen-Z, https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbescoachescouncil/2023/06/05/guiding-the-next-generation-understanding-and-leading-gen-z/
- RUIZ VÁZQUEZ, Marcela Haydée; RODRÍGUEZ GONZÁLEZ, Francisco Gabriel; TRUJILLO REYES, Juana Cecilia. Personality and leadership style in generation z: A quantitative study in a higher education institution in Mexico. Intangible Capital, [S.l.], v. 20, n. 1, p. 170-192, mar. 2024. ISSN 1697-9818. doi:https://doi.org/10.3926/ic.2383.
- Expert Panel® Forbes Councils Member, 15 Ways Leaders Can More Effectively Manage Gen-Z Workers, https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbescoachescouncil/2023/01/17/15-ways-leaders-can-effectively-manage-gen-z-workers/
- Bodunde, Wole & Johnson, & Bello, Sunday & Ade,. (2024). THE EFFECT OF GENERATION Z COMPLEXITIES ON LEADERSHIP MINDSET. 6. 62-75. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/377625470_THE_EFFECT_OF_GENERATION_Z_COMPLEXITIES_ON_LEADERSHIP_MINDSET
