Jump to the section
Key Learnings
#1
Simplify Complexity with the Right Style
Use autocratic leadership for simple projects and democratic leadership for complex, collaborative tasks.
#2
Act Fast in Crises and Task Force Projects
Adopt autocratic leadership for emergencies to ensure quick decisions and maintain control under pressure.
#3
Foster Innovation with Inspiration
Opt for transformational leadership in creative projects to inspire and empower teams for groundbreaking results.
#4
Empower Skilled Experienced Teams
Apply laissez-faire leadership for experienced teams, giving them autonomy to thrive, but ensure clear responsibilities.
In project management, successful project execution depends mainly on context, people, and results. Context gives you the characterization of project type, which results are driven by project scope.
At the center of project execution is the project team. People are delivering the results and setting the tone of the project. As a project manager, you must act also as a leader. You must continuously adapt your leadership style based on context and project scope. As a leader, you must keep the people engaged and motivated. Your leadership style as a project manager is the key factor for optimal project delivery [J. Turner et al. (2005)].
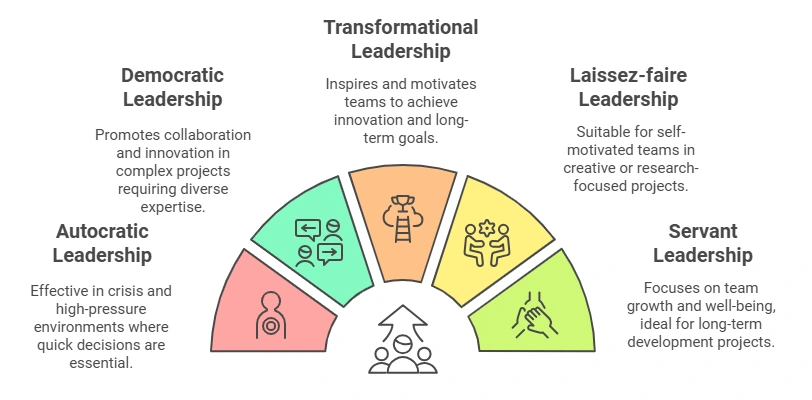
In this article, you will learn about different leadership styles and their effect on project management and delivery. You will learn which leadership style to select for each project type. Are you ready to become a better project manager and leader?

🌟 Unlock Leadership Success: Exploring Project Leadership Styles 🚀
Select Your Leadership Style for each Project Type
1. Autocratic project leadership for Crisis and Task Forces
The autocratic leadership style is when the project leader has absolute control of the decision-making and takes minimal input from the project team. It is also referred to as authoritarian leadership [Rebecca Knight, HBR (2024)].
Such a leadership style needs a leader who provides clear, specific instruction. He must dictate task distribution, and set goals and direction. Autocratic project managers can use rewards and punishment based on the established rules and project demands [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)].
It is ideal for command and control situations, where decisions are made by the project manager or a small group of experts. An autocratic leader is typically self-reliant and is based mainly on his judgments. Such a leadership style is ideal when there is no time for democratic approaches, analysis, or debates. Such projects involve crisis management and task forces. Autocratic leadership is used in emergencies, military operations, or high-pressure environments. It is also relevant in fast-paced industries, like start-up companies, where immediate action and clear direction are needed [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)], or in corporate takeover deals [Rebecca Knight, HBR (2024)].
Advantages and Disadvantages of the autocratic project leadership style
The advantages and disadvantages of autocratic project leadership are provided and need to be considered to be used in a short period and when needed [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)], [Turner, J. R. & Müller, R. (2006)], [Tamburo Michael Renzi et al. (2020)].
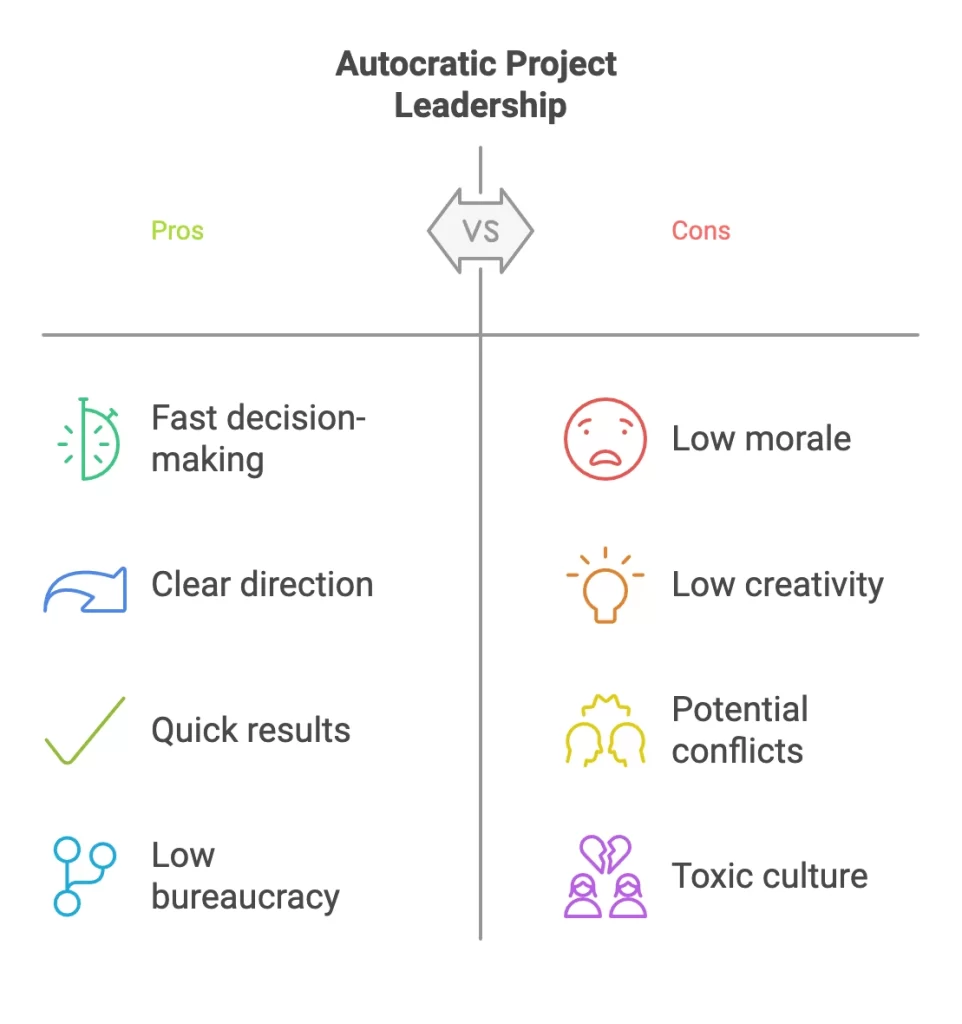
Pros of Autocratic project Leadership style:
- Fast decision-making with prompt directives: The project manager so not need to consult with the team. This can be critical in urgent situations.
- Clear direction and short communication channels: Expectations are provided directly to the team members. This is beneficial for tasks that need to be completed promptly and efficiently.
- Quick results and emergency: It is useful for crises where an immediate single direction of the team is required. This can be useful in war rooms or corporate takeovers.
- Low bureaucracy with clear roles and responsibilities: The project manager maintains control over the team, and ensures the tasks are implemented without any non-productive process.
Cons of Autocratic project Leadership style:
- Low morale and disengagement: Due to a lack of input and control from team members, team members may feel not valued. This leads to low engagement and reduced morale.
- Low creativity and innovation: The project manager limits the ability of the team members to contribute. This hinders new ideas to come up and adapt to new situations.
- Low acceptance of decisions and conflicts: This can be potential for conflicts and low acceptance of the project manager. Team members feel a lack of autonomy and respect.
- A climate of fear and toxic culture: Autocratic project managers may produce fear among team members, as they may fear to raise concerns. He is micro-managing most of the tasks, which can lead to a toxic climate in the team
2. Democratic project leadership for complex and collaborative projects
The demographic leadership style involves all team members in generating ideas, collaborating, and making decisions. It uses a shared decision-making process, and the project manager promotes social equality [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)].
The project leader collects input from all team members, and they decide based on the majority. This is ideal for complex projects, where there is a need for wider expertise and teamwork. Complex problem-solving requires innovation a combination of unique skills and multiple perspectives [gemini .google.com et al. (2024)].
Debates and constructive conflict are common in democratic-led teams. The project manager facilitates discussions, encourages participation, and incorporates feedback into decisions. This leadership style in projects requires collaboration and innovation. When the project uncertainty is high, such a collaborative approach helps to make decisions and handle complexity. Typical environments are R&D, software development, and projects with cross-functional teams [Muhammad Abrar Ahmed et al. (2023)].
Advantages and Disadvantages of the democratic project leadership style
The advantages and disadvantages of democratic project leadership are provided and can be applied to specific project phases, where uncertainty and complexity are high [Muhammad Abrar Ahmed et al. (2023)], [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)], [M. Sousa et al. (2017)].
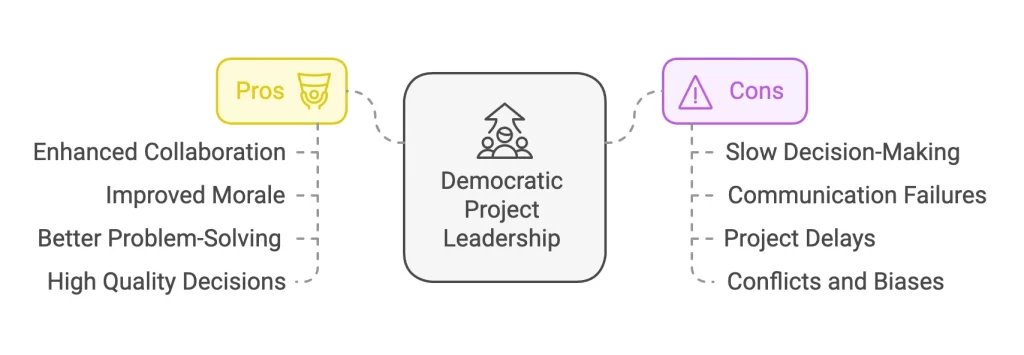
Pros of democratic project Leadership style:
- Enhanced collaboration and engagement: Team members feel heard and valued by the democratic project manager. They feel respected and have a sense of ownership. This improves the sharing of ideas and opinions and leads to higher team engagement.
- Improved team morale and cohesion: The psychological safety of sharing ideas and speaking up is important. Team members feel responsible for the results and the decisions. This leads to stronger team bonds and better team pride in results.
- Better Problem-Solving: By hearing multiple perspectives and using unique skills from the team, complex problems can be solved better. Multiple solutions are generated and combined into the final one from the experts. Innovation and creativity are essential for solving complex problems and uncertainties.
- High Quality of Decisions: Decisions are well-rounded by all team members and consensus is promoted. This social responsibility for decisions in the team improved the quality and accelerated the execution of team decisions.
Cons of democratic project Leadership style:
- Slow decision-making process: Reaching consensus can be time-consuming. It can lead to lengthy processes, including debates and multiple people and opinions. This makes the progress feel slower. Decisions need to be documented and reduce speed while increasing effort.
- Communication failures: Such a democratic approach from the project manager can lead to unclear direction and goals. Project managers seem to facilitate and not lead in a single direction.
- Delays in project delivery: Many opinions can lead to loops and delays in the development phase. This can lead to delayed or uncompleted projects when the schedule is of great importance. It is not recommended in a crisis.
- Conflicts and Biases can arise: Conflicts can arise if a team member is assertive or a non-team player. If the team is also lacking expertise and is based on a single expert, the team can be biased from her opinion.
3. Transformational project leadership for innovation and dynamic projects
Transformational project leadership focuses on inspiring, motivating, and engaging team members toward a greater mission or long-term roadmap [Muhammad Abrar Ahmed et al. (2023)]. It requires a higher level of engagement, innovation, and commitment from the project team.
Transformational leadership is used when innovation and bigger organizational changes need to be implemented. Transformation requires engagement in new ways of working and acceptance of new ways of working. Project managers must stimulate creativity and innovation, through a sense of ownership and commitment. The project leader must articulate a clear vision and inspire team members to contribute towards this vision and roadmap [gemini .google.com et al. (2024)].
Transformational project leaders inspire teams to think of new ways of working and solutions [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)]. It can be beneficial for projects that improve business processes and improve productivity and profitability. Innovation projects, like product development, can also enjoy the transformational leadership style. Change management and collaboration are the main skills required from the project manager.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the transformational project leadership style
The advantages and disadvantages of transformational project leadership are provided. Such leadership style must be used if changes or a new vision are required to be implemented through project delivery [Muhammad Abrar Ahmed et al. (2023)], [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)], [Tamburo Michael Renzi et al. (2020)], [M. Sousa et al. (2017)].
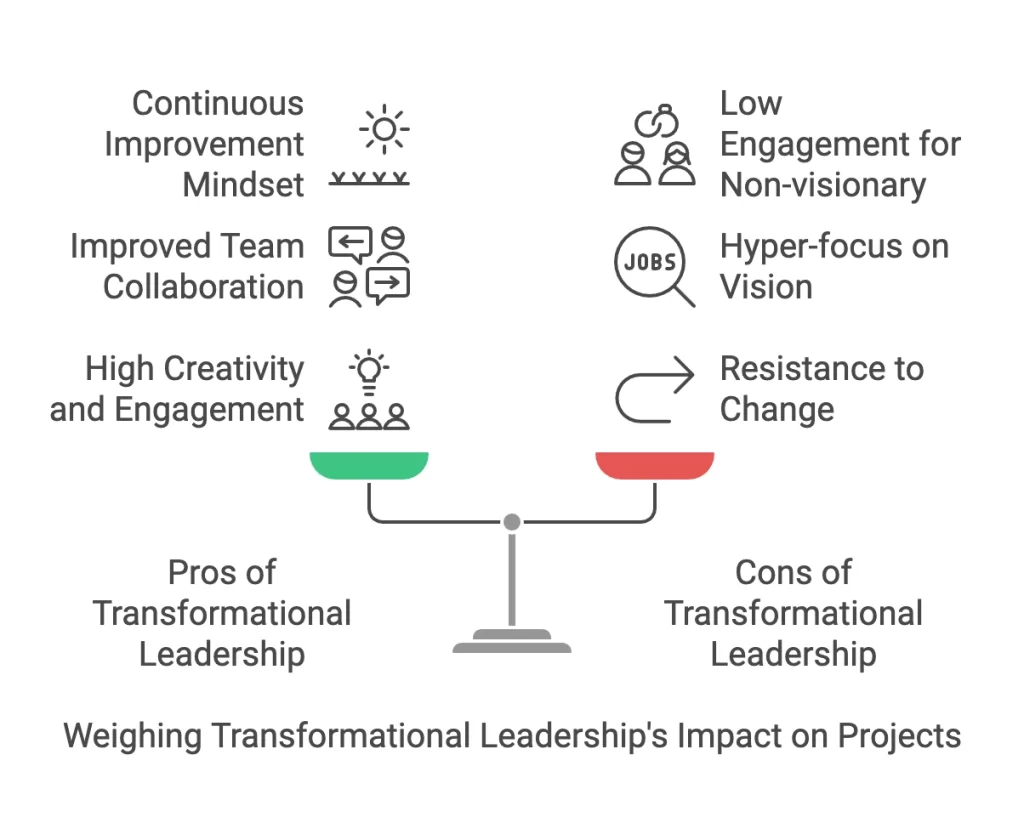
Pros of Transformational Project Leadership style:
- High Creativity and Team Engagement: Transformational project leaders create a sense of urgency and purpose. This leads to higher engagement and innovation. Project leaders promote a culture of experimentation and a failure-safe environment.
- Improved Team Collaboration: The project manager encourages collaboration and teamwork approaches. New ways of working and new ideas are promoted as project results. This leads to higher acceptance, team collaboration, and job satisfaction.
- Continuous Improvement Mindset: Transformational project leaders strive to change and improve the status quo. This mindset leads to long-term growth for the team, and such leaders encourage positive outcomes and improvements to processes.
- Greater Competence and Efficiency: All the changes, learnings through experimentation, and collaboration lead to improving team competencies. The team is improving processes and becoming more efficient independently. Transformational leaders often develop other leaders in project teams.
Cons of Transformational Project Leadership Style:
- Delays due to resistance to change: Team members or stakeholders can create delays if they do not accept new ways of working or solutions. Change and stakeholder management skills are required to overcome such obstacles.
- Hyper-focus on vision: Transformational project leaders may focus on long-term vision and lose details on project execution. Short-term goals may be missed, which can create lost project momentum and lower morale.
- Low engagement for non-visionary: Not all people may believe in the vision, which can create low engagement and resistance. Project leaders need to define strict deadlines and clear goals for such team members or stakeholders.
- Limit creativity due to uncertainty and dynamic environment: If the team is not managed correctly, uncertainty can lead to chaos and uncertainty. This creates interpersonal obstacles and limits creativity among team members. Leaders must put structure and offer a “fail-safe” environment.
4. Laissez-faire Project leadership for research projects with self-motivated teams
Laissez-faire project leader has a hands-off approach, where she delegates tasks and provides minimal direction or intervention. Project teams have the complete rights, power, and freedom to decide on their tasks or work packages [Muhammad Abrar Ahmed et al. (2023)], [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)].
The project manager provides direction and allows team members to make their own decisions on how to achieve results. This leadership style works for teams with highly skilled and self-motivated members. It can work for projects in creative industries, academic research, and start-ups with experienced professionals.
The role of the laissez-faire project leader is to provide support and resources when needed. In all other aspects, team members are autonomous and can operate independently. This leadership style is ideal for projects where autonomy and self-rule are important for team members [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)]. Team members take full pride in their work and are self-driven in delivering project results.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Laissez-faire project leadership style
The advantages and disadvantages of Laissez-Faire project leadership are provided. Such leadership style must be used only in mature and highly experienced project teams. It is like a double sword, can be empowering but if the conditions are not right can lead to chaos [gemini .google.com et al. (2024)], [Tamburo Michael Renzi et al. (2020)], [M. Sousa et al. (2017)].
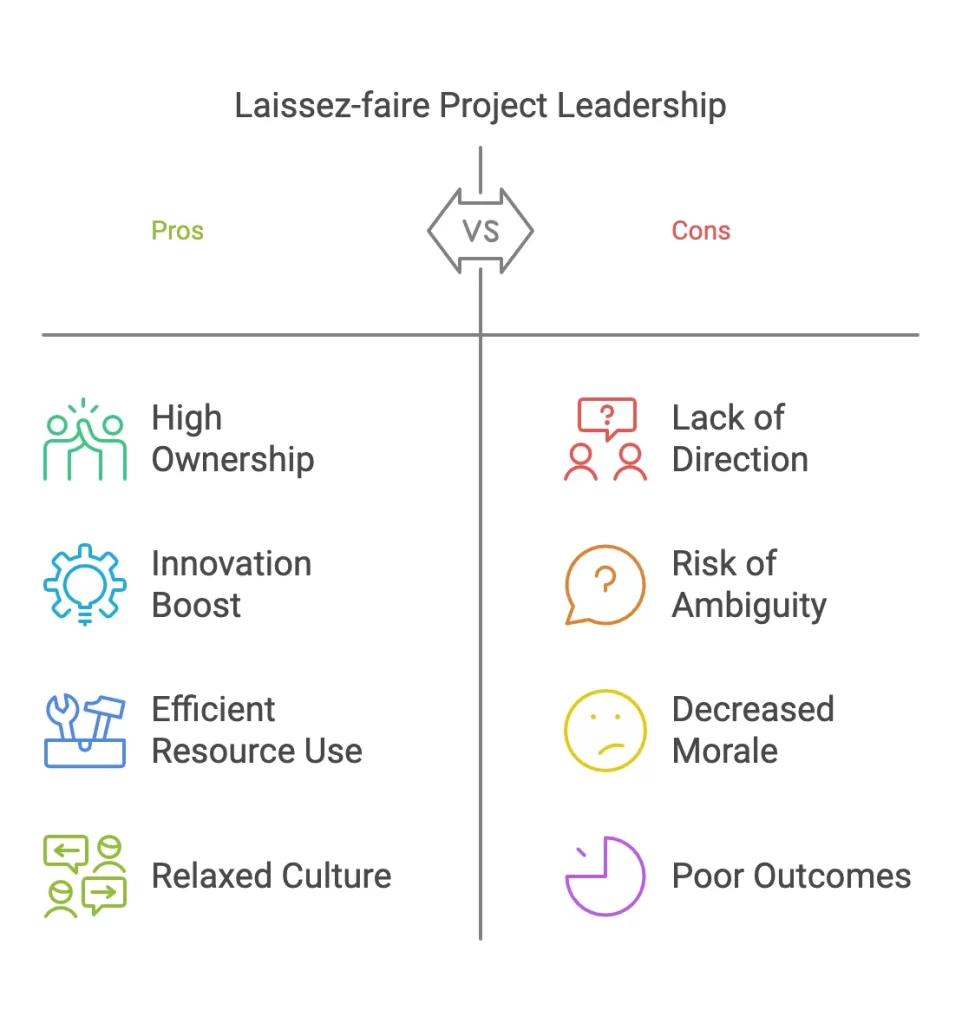
Pros of Laissez-Faire Project Leadership style:
- High Ownership and Empowerment: Team members enjoy a high degree of freedom to make decisions. Teams of experienced professionals feel empowered and proud of their results. Self-motivation of such experienced professionals is rather high.
- High levels of innovation and job satisfaction: Creativity can be highly improved with laissez-faire project leadership if the individuals have the right skills and expertise. Autonomy can foster a fail-safe environment, which leads to innovation and high job satisfaction.
- Efficient use of Resources and Expertise: Team members need to be experts in their domain and self-motivated. This means that they can decide how to use their resources to produce project results. The decision-making process is efficient but is heavily dependent on such individuals.
- Relaxed Organizational Culture: A highly independent project team with minimal oversight leads to a relaxed and flexible work environment. This can be advantageous for creative businesses, such as product design and advertising agencies.
Cons of Laissez-Faire Project Leadership Style:
- Lack of direction and reduced accountability: Disorganization and project delays from members with low self-discipline can happen. Lack of a definition of clear roles and responsibilities can lead to conflicts misunderstandings and confusion for less experienced team members.
- Risk of ambiguity: Communication issues could arise due to a lack of centralized organization. This can hinder project progress due to insecurity or lack of clarity.
- Potential decrease in team morale: Conflicts between team members can arise if they are not managed efficiently. Team members with an assertive style can create issues with communication and ownership of results.
- Poor outcomes due to lack of leadership: This project leadership style is not suitable for less mature and experienced teams. It can lead to poor project outcomes or low-quality deliverables.
5. Servant Project Leadership for long-term development projects
Servant project leadership style focuses on the growth, development, and well-being of team members. The project leader focuses more on the relationships with the team, showing empathy, active listening, and stewardship [gemini .google.com et al. (2024)]. Such a servant project team leader creates an environment where all team members feel valued and empowered.
This style is effective for long-term development projects. Such projects need sustained motivation and commitment over longer periods. Team cohesion and morale are important for project performance. The project manager supports and develops the skills of team members, rather than exerting authority. His role is mainly removing barriers and empowering team members to execute tasks.
It is mainly used where trust, collaboration, and ethical behavior are required for the type of project or organization [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)]. It is a people-centric approach and therefore is applied mainly for projects in community development, education initiatives, and healthcare projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Servant Project Leadership Style
The advantages and disadvantages of servant project leadership are provided. Such leadership style must be used in mature project teams that focus on long-term growth instead of tight schedules [gemini .google.com et al. (2024)], [Tamburo Michael Renzi et al. (2020)], [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)].
Pros of Servant Project Leadership style:
- Strong relationships, loyalty, and empathy: A servant project leader is also called a people leader. This can create strong bonds among team members and project leaders. Team members are loyal and show a higher degree of empathy.
- Increased motivation and engagement: A supportive environment can bring high team engagement. By prioritizing growth and well-being, servant project leaders can empower them to take ownership of their work. This boosts motivation and team morale.
- Improved productivity: Servant project leader has a special focus on teamwork and collaboration. Communication in the team improved due to strong relationships, and therefore productivity of team members.
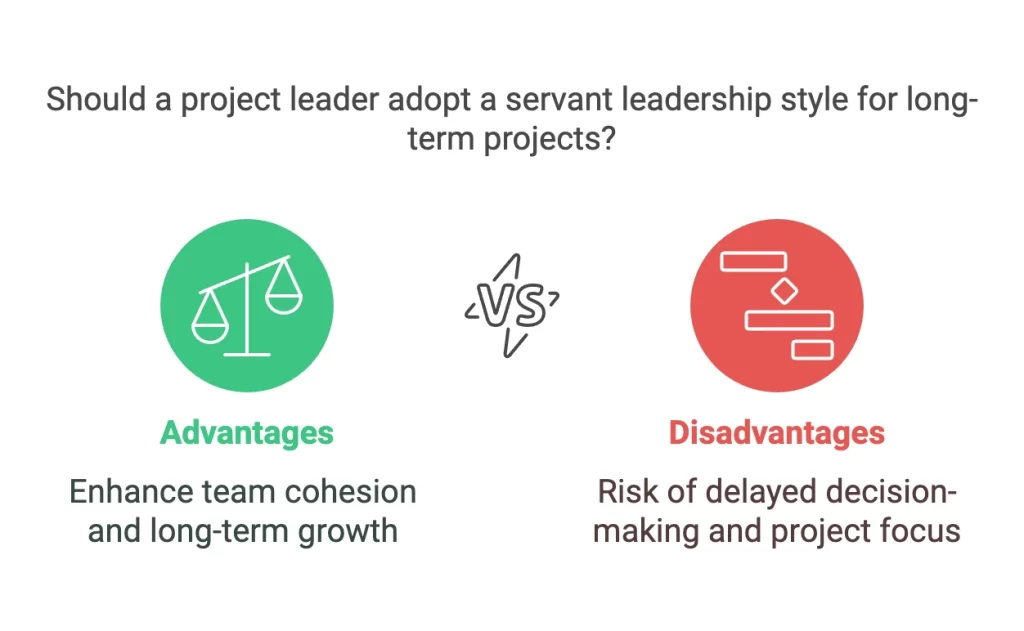
- Fosters long-term growth: A servant project leader is focusing on building a strong ethical environment based on trust and open communication. This improved the long-term growth of team members and better alignment with stakeholder needs.
Cons of Servant Project Leadership Style:
- Slower decision-making: A servant leader may be focused on longer debates and this can slow the decision-making process. This is due to a high focus on people and consensus-building, instead of results and project progress.
- Lack of focus on project deliverables: Focusing on the team’s needs can bring a lack of focus on project deliverables. This can lead to a possible lack of project direction and discipline of team members. Therefore this project leadership style requires highly disciplined team members.
- Project delays due to lack of sense of urgency: A servant project leader is people-oriented and may not address schedule pressure accordingly. This comes from a priority on relationships rather than results.
- Conflict management can be challenging: Resolving conflict among team members can be a challenging task for a servant project leader. He has to make decisions and resolve the conflict without consensus. Project results can suffer if the conflicts are not addressed promptly.
Leadership Qualities for Successful Project Delivery
Project leadership style is an important factor for the successful project delivery. Numerous projects are failing due to the wrong type of leadership. A leader must create the right environment where all team members can excel.

A project leader is also a project manager, who can be able to provide structure, coordinate activities, and break-down project scope. A leader must create cohesion in the project team and “sense” the needs of the project for optimal delivery. The project leader must apply the leadership style that is required [Rebecca Knight, HBR (2024)].
This requires specific skills and leadership qualities from the project manager [Alaba Adetola et al. (2023)]:
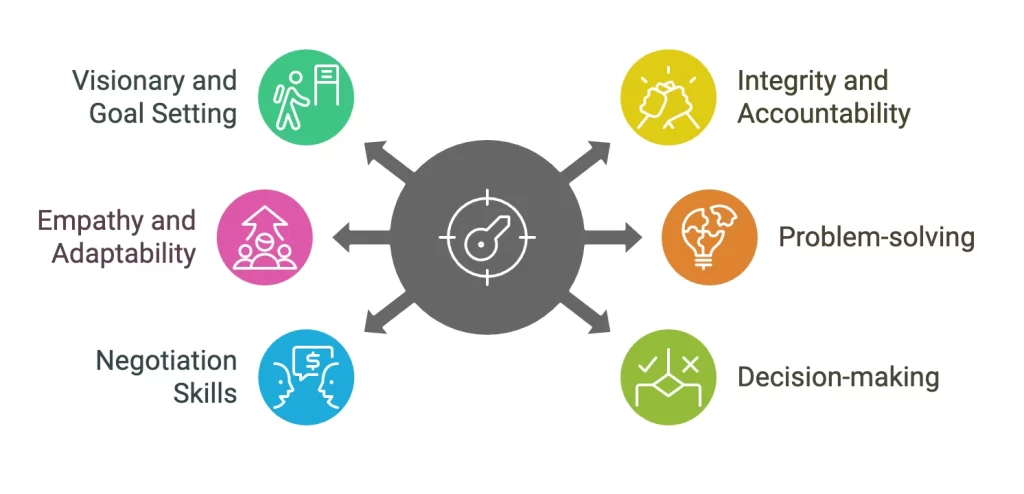
- Visionary and Goal Setting: A project leader should define clearly the goals and project direction. All team members and stakeholders must be aligned with the common vision.
- Integrity and Accountability: Project leaders should accept responsibility for their activities and be transparent. They should bring trust through honesty and consistent behavior.
- Empathy and Adaptability: The project leader needs to be open to changes and adapt plans according to the needs. He should be able to understand the needs and feelings of the team to provide motivation and focus.
- Problem-solving: Project leaders should have technical knowledge. They should be able to predict and address problems. They should be able to analyze and evaluate project issues objectively.
- Negotiation skills: Project leaders should have negotiation skills for resolving differences and conflicts between stakeholders and team members.
- Decision-making: They should be able to make strong decisions, using the right leadership type. Risk Management is part of the decision-making process. Leaders should be able to assess and mitigate risks in decisions.
Align your leadership style with the project type for optimal delivery
Leadership style should be tailored to the specific needs of the organization and the project type. In a crisis, a time-sensitive project, or a complex collaborative team effort, it is important to know how your leadership affects team performance and results delivery.

By aligning your leadership style with the characteristics of your project, you can maximize your chances of success. Effective project delivery is all about leading people. Applying the right leadership style you can ensure successful project delivery and high stakeholder satisfaction.
FAQs
Autocratic leadership is ideal for crisis management as it ensures fast decision-making and clear directives. It centralizes control with the project leader, which is crucial in high-pressure situations like emergencies or corporate takeovers.
Democratic leadership is best suited for complex and collaborative projects that require innovation, teamwork, and multiple perspectives, such as R&D or software development.
Transformational leadership inspires creativity, collaboration, and continuous improvement. It is particularly effective for innovation projects or those requiring significant organizational change.
Laissez-faire leadership can lead to ambiguity, reduced accountability, and poor outcomes if team members lack experience or self-discipline. It is most effective with mature, self-motivated teams.
Key qualities include visionary goal-setting, integrity, adaptability, problem-solving skills, effective decision-making, and the ability to align leadership style with project needs.
References
- J. Turner et al. “The Project Manager’s Leadership Style as a Success Factor on Projects: A Literature Review.” Project Management Journal, 36 (2005): 49 – 61. https://doi.org/10.1177/875697280503600206.
- Muhammad Abrar Ahmed et al. “Leadership Styles and Their Influence on Project Team Performance.” sjesr (2023). https://doi.org/10.36902/sjesr-vol6-iss2-2023(153-159).
- gemini .google.com et al. “Leadership Styles and Their Influence on Project Team Performance.” Non human journal (2024). https://doi.org/10.70008/nhj.v1i06.29.
- Alaba Adetola et al. “Impact of Leadership Styles and Qualities on Project Lifecycle.” International Journal of Innovative Business Strategies (2023). https://doi.org/10.20533/ijibs.2046.3626.2023.0077.
- M. Sousa et al. “Project Managers Perceptions about more Effective Leadership Styles.” Journal of international business research, 2 (2017): 7-13. https://doi.org/10.18775/JIBRM.1849-8558.2015.23.3001.
- Wilfred Uwguanyi et al. “Effect of Project Leadership Styles on Organizational Performance.” Journal of Management and Social Science Research (2023). https://doi.org/10.47524/jmssr.v4i2.50.
- Tamburo Michael Renzi et al. “The Effect of Leadership Styles on Project Implementation.” Open Journal of Leadership (2020). https://doi.org/10.4236/ojl.2020.94012.
- Rebecca Knight, HBR (2024), 6 Common Leadership Styles — and How to Decide Which to Use When, https://hbr.org/2024/04/6-common-leadership-styles-and-how-to-decide-which-to-use-when
- Turner, J. R. & Müller, R. (2006). Matching the project manager’s leadership style to project type. Paper presented at PMI® Research Conference: New Directions in Project Management, Montréal, Québec, Canada. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute. https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/matching-project-managers-leadership-style-8055
