Jump to the section
- Key Learnings
- What is an Agile Organization?
- What is Agile Transformation?
- Why Implement an Agile Transformation?
- Benefits of Agile Transformation
- Challenges of Agile Transformation
- Steps to Implement Agile Transformation
- 10 Key Factors for Successful Agile Transformation
- Agile Transformation is an ongoing journey
- FAQs
- References
Key Learnings
#1
Learn how to do Agile Transformation
Agile transformation is a holistic change that shifts an organization’s culture, mindset, and processes, enabling flexibility, adaptability, and continuous value delivery.
#2
Benefits of Agility
Agile methods help organizations respond to change quickly, reduce time-to-market for products, and improve customer satisfaction by prioritizing collaboration and continuous improvement.
#3
Steps for Success
Key steps include defining a clear vision, empowering cross-functional teams, implementing iterative pilot projects, and aligning agile practices with organizational goals.
#4
Addressing Challenges
Resistance to change, cultural barriers, and scaling issues requires leadership commitment, effective communication, and a customer-centric focus.
Does your organization struggle with responding to dynamic market demands quickly enough? Through agile transformation, you can become competitive and be successful in the state of continuous change. That includes changing the culture, mindset, and methods of one’s organization and not just mere processes. This would render your organization flexible enough to deliver value consistently [Manubrahma et al., 2024], [Gren & Lenberg, 2019].

This article discusses how to lead a successful agile transformation, from creating a clear vision to empowering teams and overcoming common challenges. Agile methods such as Scrum and Kanban give a framework for iterative development, collaboration, and adaptability. The leaders and teams involved in the process are therefore able to respond rapidly to market changes to improve customer satisfaction and drive innovation [Amajuoyi et al., 2024], [Helmlinger, 2023].
You will learn practical strategies and actionable insights to help your organization adopt agility without losing focus on goals. By adopting an agile mindset, your organization can become a role model for responsiveness and efficiency in meeting your goals.

🚀 Mastering Agile Transformation: Unlock Your Organization
What is an Agile Organization?
Agility means embracing change by fusing adaptability, innovation, and a strong customer-centric orientation in the organization. Contrary to traditional businesses that depend on rigid hierarchies, an agile organization is well-structured and dynamic. It is fast-moving without losing stability and effectiveness since it is a tradeoff crucial for sustainability in the long term [Brosseau et al., 2019].
An agile organization must be customer-centric. All decisions, processes, and goals are defined for delivering value to customers. This ensures that an organization stays relevant and competitive in a dynamic environment [De Smet et al., 2018].
How do Agile Organizations Differ from Traditional Organizations?
Traditional organizations are usually based on static, siloed structures where decisions flow top-down. Agile organizations operate as flexible networks with empowered teams. These teams have the autonomy to make decisions based on real-time data. It allows for quicker and more accurate responses to changing conditions [Brosseau et al., 2019].
While traditional models focus on control and hierarchy, agile organizations emphasize collaboration and learning. They replace rigid structures with scalable networks supported by a stable backbone that provides clarity and consistency while allowing for fast change [De Smet et al., 2018].
Agile Organization Priorities
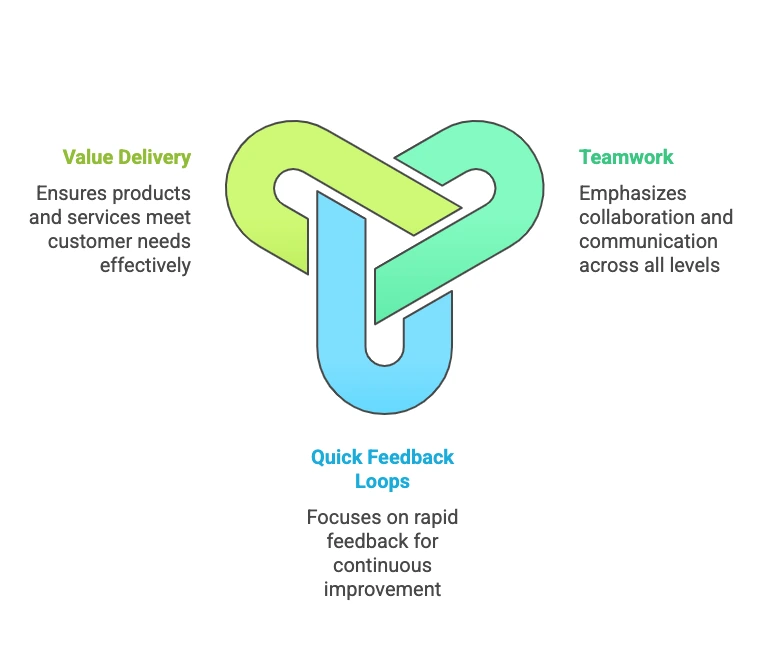
- Teamwork: Teams work together as one across all levels while maintaining a solid alignment and open communication.
- Quick Feedback Loops: Agile organizations accord much priority to getting rapid customer and stakeholder feedback, enabling the organization to continuously improvise [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
- Value Delivery: The focus is on delivering customer value and ensuring that products and services can meet real-world needs effectively and efficiently.
Efficiency and Effectiveness in Agile Organizations
Agile organizations, through iterative cycles and by empowering teams to learn and adapt quickly, have an edge in developing products quickly and in the dynamic allocation of resources to make sure efforts are directed where they will have the biggest impact [Brosseau et al., 2019].
Through real-time data, agile organizations can decide much quicker and at the same time establish a stable base for a coherent operation. Taken directly together, the dynamism and stability ensure that technological advancement and changes in the markets can be coped with as little disruption as possible [De Smet et al., 2018].
Key Building Blocks of an Agile Organization
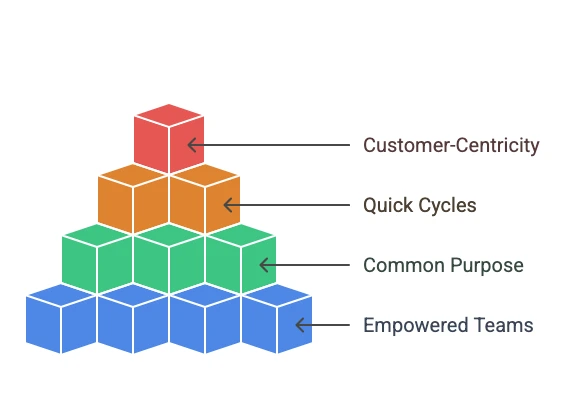
- Empowered Teams: Small, autonomous, and cross-functional teams that deliver results
- Common Purpose: A shared “north star” vision aligns the organization in purpose and direction.
- Quick Cycles: Agile organizations have short cycles allowing them to respond quickly to data on performance and customer feedback.
- Customer-Centricity: All the decisions and processes are centered on understanding and meeting customer needs.
Why Agile Organizations Succeed
The agile organization succeeds with the combination of speed, flexibility, and customer focus. With the aid of empowered teams and continuous feedback loops, it adapts to market demands on top of a stable base for growth. The approach drives innovation, creates resilience, and guarantees that the customer is at the core of every decision.
What is Agile Transformation?
Agile transformation is the holistic change in the way organizations function, away from rigid and traditional ways and toward flexibility and adaptability. This change is neither superficial nor a localized adjustment in the organization. It takes it to much deeper levels through a reorientation of its processes, cultural norms, and mindsets in competing successfully in the dynamic markets [Daraojimba et al., 2024], [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
Agile transformation requires the creation of an agile mindset. It is the mindset that collaboration, flexibility, and experimentation at all levels of an organization are brought. Leaders can easily integrate these values by ensuring that there is always continuous learning about customers [Manubrahma et al., 2024], [De Smet et al., 2018].
Main Principles of Agile Transformation
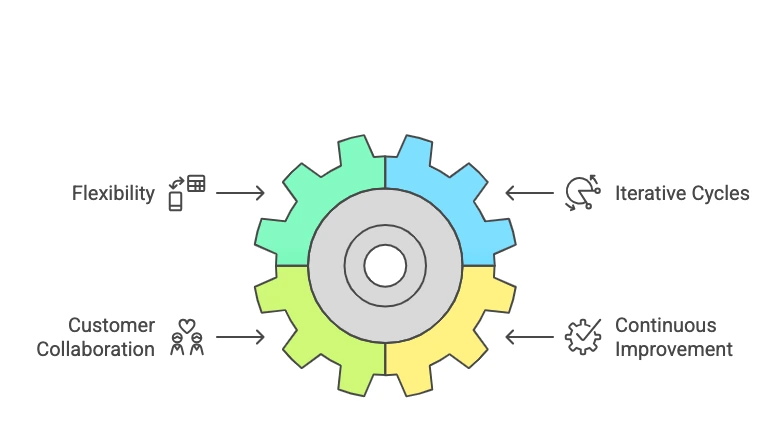
- Flexibility: A principle of agile is flexibility. It is the ability to quickly pivot in case market conditions change, customer needs shift, or new technologies emerge. It is the opposite of long-term, static plans that rely on real-time decision-making in dealing with contemporary challenges [Gren & Lenberg, 2019].
- Iterative: Agile project management methods, such as Scrum and Kanban, focus on continuous iterative cycles. These are implemented in sprints and releases. Such an iterative approach allows the team to deliver small pieces of value more frequently. It brings customer feedback into the process continuously and efficiently. This ensures better alignment with customer expectations [Popoola et al., 2024].
- Customer Collaboration: Agile development involves the customer in the development process. This will ensure that solutions are relevant to the real needs, building trust and driving continuous improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: One of the major characteristics of agile development involves continuous reviewing and improving the processes. This is where the team actively seeks opportunities how to drive improvements toward sustainability and growth [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
Responsiveness is the Heart of Agile Transformation
In a nutshell, agile transformation means responsiveness to change; in other words, the ability to react swiftly and effectively to any external factors—be it market shifts, customer demands, or technological disruptions—is the major attribute of agility. While the traditional approaches stick to rigid and fixed plans, agile models can thrive in an environment of welcome changes, where challenges are looked at as opportunities [Gren & Lenberg, 2019].
Why Implement an Agile Transformation?
With the continuous changes in technology, globalization, and customer expectations, agile initiatives have become a ‘must’ for any organization. Traditional methods can hardly keep up with changes at such high speeds; therefore, adaptability and flexibility become very important means of survival.
Implementation of agile initiatives allows businesses to adjust easily to market dynamics and respond efficiently to emerging opportunities to make sure that they remain not only relevant but also resilient [Popoola et al., 2024].
Meeting Market Demands with Agility
The very basis of agile initiatives is responsiveness to market demand. These methodologies allow organizations to respond easily to evolving consumer preferences and industry trends. With a sudden shift in customer needs, agile practices ensure that businesses can pivot without losing momentum. Agile methodologies give organizations the flexibility needed to deliver solutions that match up to real-world demands and therefore secure a strong presence in dynamic markets [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
Driving Competitiveness and Innovation
Agile initiatives drive competitiveness to a large extent. Iterative development helps organizations launch products to the market fast, thereby gathering feedback from the market and making the product much more precise. That gives an open competitive advantage to such firms to be ahead of their competitors. Agile practices foster innovation because cooperation among diverse teams could be augmented, developing an environment where creativity might thrive [Amajuoyi et al., 2024]. This combination of adaptability and innovation allows companies to constantly create value [Tshabalala & Marnewick, 2021].
Benefits of Agile Transformation
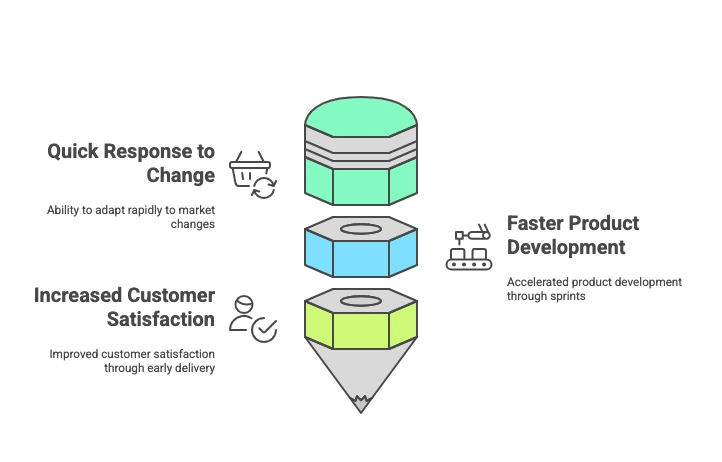
Respond Quickly to Change
Its most value for organizations is its application in the ability of transformations to make organizations adapt rapidly to change. Agile approaches attach inherent worth to changing requirements, even in some later stage of development, and convert possible change into opportunity. This is most useful in business environments with dynamic turbulence that change things overnight in market trends and what customers want [Daraojimba et al., 2024]. Agile processes have flexibility in the fact that it does not insist on needing to follow the plan rigidly as in traditional ways but rather look at how to use change as a tool for competitive advantage [Al-Saqqa et al., 2020]. For instance, in times of sudden market change, companies have successfully maneuvered their development activities to adjust their offering [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
Faster Product Development
By iteration cycles called sprints, agile transformation accelerates product development. Team members deliver part of the product within short timelines and this makes the organization faster to market [Daraojimba et al., 2024]. It was discovered that agile practices generally shorten development cycles by 30-40% hence they would be earning the fastest time to market. This is a competitive element for most such organizations. One example of an application is that many technology companies release beta versions within weeks, gathering user feedback and keeping on fine-tuning their products for consumers’ requirements [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
The Increased Satisfaction of Customers
The basic transformation in agile is that it improves customer satisfaction. Early and continuous delivery of important and useful products meets customer needs better under agile methodologies [Daraojimba et al., 2024]. Agility is all about customer satisfaction-early and continuous delivery of valuable products: the products end up meeting needs better.
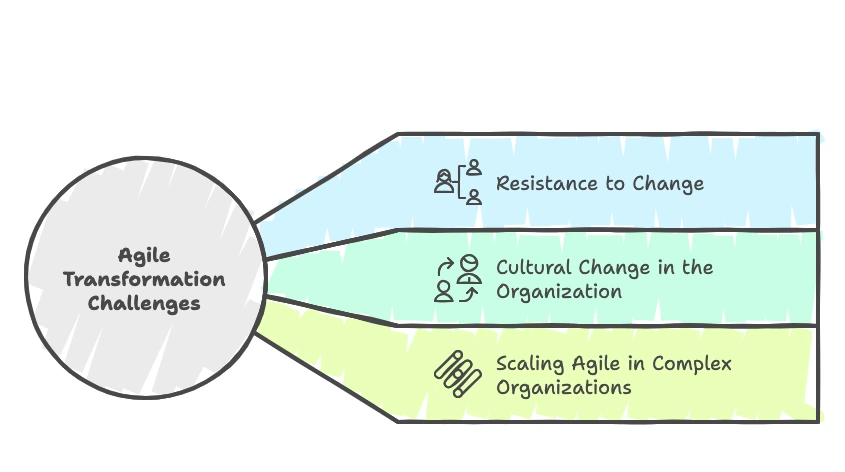
Challenges of Agile Transformation
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change becomes a critical barrier to the implementation of an agile transformation. A majority of employees will not break free from traditional hierarchical structures and sequential workflows, very familiar and secure [Manubrahma et al., 2024]. Such conflict breaks by redefining roles and responsibilities, which usually induces undefined confusion and skepticism among team members. Such resistance is fueled by the representatives through an understanding deficit, fear of influencing loss, or simply discomfort with operations they are not familiar with. For instance, teams used to inflexible roles would very likely resist change into collaborative, self-organizing structures, thus slowing down the process of taking such an initiative [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
Cultural Change in the Organization
Changing the organization in the direction of agile values has been one of the toughest aspects of agile adoption. Agile emphasizes collaboration, empowerment, and flexibility. These values do not fit in with the traditional top-down management approaches [Manubrahma et al., 2024]. However, it takes more than just new processes to change values, behaviors, and mindsets; it needs sustained effort and commitment from one’s leaders. Leadership will build a culture based on trust and continuous improvement, where employees have the power and ownership to take responsibility for their actions. For instance, cultural resistance will lead to impeding and partially successful implementations [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
Scaling Agile in Complex Organizations
Without a doubt, scaling agile in huge, ambiguous firms complicates matters further. Agile principles, originally formulated for small teams, often need a major adaptation to be effective in the broader organizational context [Daraojimba et al., 2024].
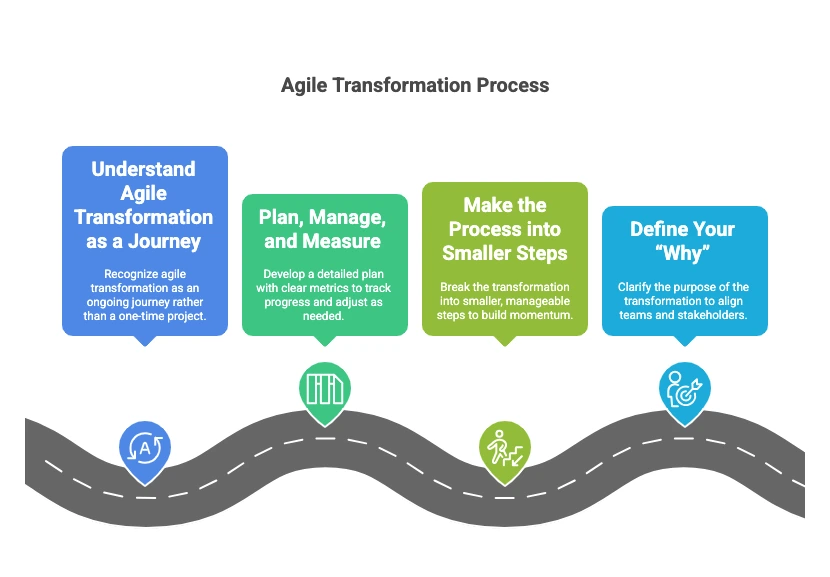
Steps to Implement Agile Transformation
Step 1: Understand Agile Transformation as a Journey
Agile transformation is a process rather than a one-off project. Continuous adaptation and learning are required, to grow along with the organization. Rather than end-stopping, commit to iteratively. Engaging in the mindset makes it easier for companies to confront challenges and refocus strategies properly. They turn out to be exemplary companies that always consider transformation to be a learning journey; thus, they end up being much more agile and resilient than others [Brosseau et al., 2019].
Step 2: Plan, Manage, and Measure
Create a detailed plan that will transform the clear metrics into tracks of progress and stages of transformation through which business value will consistently be realized [Zack, 2023]. Identify goal standards for every stage and measure results for adjustment where required. In that way, organizations would get better results, such as increased efficiency, and higher team alignment. So when different organizations implement such well-designed KPIs for tracking transformation [Amajuoyi et al., 2024], [Zack, 2023].
Step 3: Make the Process into Smaller Steps
Try to implement small steps to reduce complexity and build momentum. Focus on quick wins rather than managing your team over the long run. This will help the organization to accept bigger transformation changes [Maule, 2024]. For example, test out agile practices in selected teams or departments, allowing the organization to refine its approach before scaling, which increases the chances of long-term success [Zack, 2023].
Step 4: Define Your “Why”
Clarify the purpose of your agile transformation and properly align teams with stakeholders. Clear “Why” informs and ensures agility is in the bigger picture of the organization. For example, they shared a unified goal to improve the speed of delivery, thereby mobilizing teams toward commitment and streamlining decision-making. [Maule, 2024].
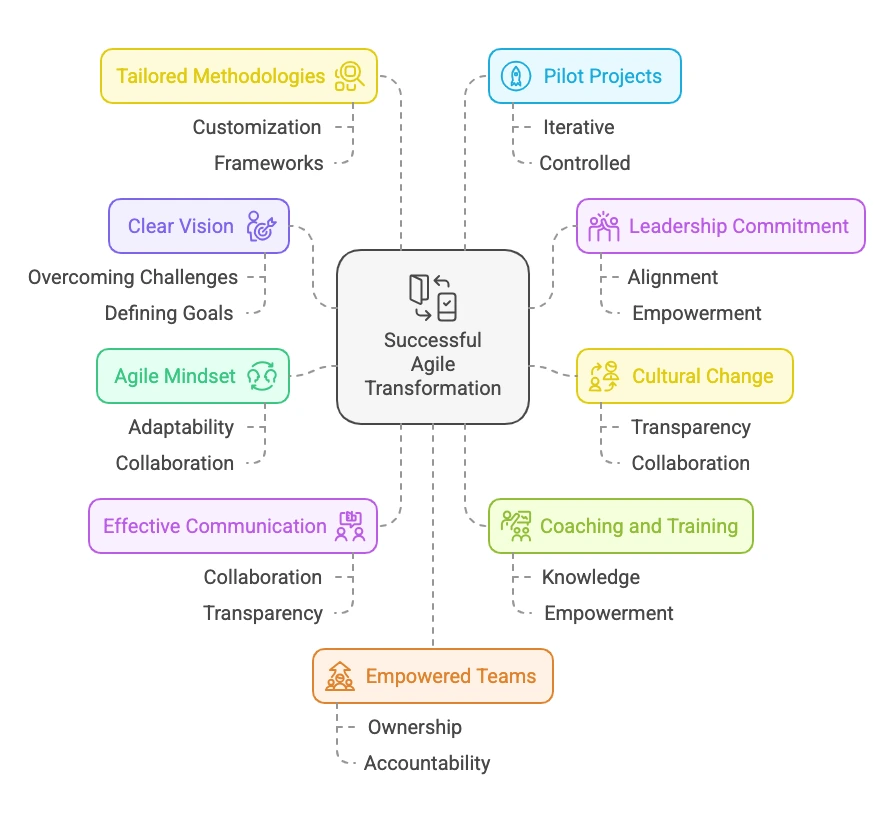
10 Key Factors for Successful Agile Transformation
1. Start with a Clear Vision
The transformation into agility needs to start with a really clear, compelling vision focused on overcoming current challenges, having some defined, measurable set goals such as a 30% reduction in time to market or a 15% improvement in customer satisfaction. Such a vision guarantees alignment with strategic objectives because it tends to create commitment as well as measurable progress [Pacheco-Cubillos et al., 2024].
2. Take Commitment and Alignment of Leadership
Strong aligned leadership is of great importance in bringing about successful agile transformation. Leadership has to make a move from being directors but instead, give teams a sense of belonging in decision-making and collaboration. They should urge their teams to embrace lifelong ways of change by modeling agile behaviors such as transparency and participation in agile ceremonies [Brosseau et al., 2019], [Zack, 2023].
3. Focus on Cultural Change
Transformation towards Agile success requires mega cultural change by enabling rigid structures at a hierarchical level substituted with collaborative structures where values of transparency, flexibility, and continuous improvement are prevalent, courageousness to experiment and learning by failures enables team adaption with speed and delivery to the value of consumers in a simultaneous grow of the same agility level by levels within an organization [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
4. Build Agile Mindset
Agile, in essence, means being adaptable, collaborative, and delivering value iteratively. Change is one of the crucial drivers to which exposure will lead to understanding how value creates and executes products. It inspires agile behaviors in teams, responding swiftly to changes in markets and customer feedback, focusing on responsiveness to changes in priority to ensure compatibility of innovation with needs and growing with an advantage over competition [Gren and Lenberg, 2019].
5. Prioritize Effective Communication
Agile thrives on effective communication to ensure collaboration and transparency across teams. Progress is kept visible, and challenges are addressed quickly with tools like daily stand-ups and sprint reviews. Setting up strong communication channels ensures the sharing of ideas, feedback, and alignment, which boosts team productivity and project success [Amajuoyi et al., 2024].
6. Invest in Coaching and Training
Training ensures that teams understand agile principles. Coaching empowers the team to put these practices into action. The role of an agile coach or Scrum Master helps to guide teams in their adaptability and solve daily challenges. Internal coaches tailor the agile framework for the organization in line with organizational goals, ensuring a tailored and sustainable transformation [Brosseau et al., 2019].
7. Tailor Agile Methodologies
The right agile approach must be selected; frameworks like Scrum, Kanban, or hybrid models have to be aligned with the organizational needs of an organization. Customizing the methods makes them fit the project size, team dynamics, and industry specifics while holding onto core agile principles such as collaboration and flexibility. Designed frameworks maximize effectiveness without compromising on agility [Daraojimba et al., 2024].
8. Iterate on that—begin with pilot projects
Agile transformation thrives in an iterative process. Start with pilot projects to prove and refine the methodologies in a controlled environment, then continue iteratively to adjust and improve while rolling out changes in phases. This approach can mitigate risks, build confidence, and ensure that agile transformation goes smoothly [Helmlinger, 2023].
9. Build and Empower Agile Teams
Building small cross-functional teams with clear roles improves collaboration and efficiency. These teams should be empowered to make decisions independently. They must have a sense of ownership and accountability. Empowered teams can lead to a successful agile transformation. They can show better cohesion and improved relationships [Daraojimba et al., 2024], [Gustavsson et al., 2022].
10. Ensure Transparency and Adaptability
Transparency can build trust in the team. This can be achieved by sharing team goals, showing progress, and discussing challenges. Clear communication of agile benefits concerning company objectives encourages collaboration. This calls for adaptability—teams must adapt to the market changes and ride on new opportunities while ensuring responsiveness at all levels of the organization [Amajuoyi et al., 2024], [Gren & Lenberg, 2019].
Agile Transformation is an ongoing journey
Agile transformation is a continuous journey. It requires commitment, adaptability, and collaboration at every level within the organization. The key to providing innovation and improving customer satisfaction lies in empowering teams. Leaders must embrace transparency, and adapt their leadership styles.

Challenges will arise, but the rewards of faster delivery, flexibility, and improved outcomes make the effort indispensable. Start small, stay aligned to agile principles, and ensure goals are measurable to sustain momentum. The path to an agile organization is strategic toward sustainable success. Dive in and find out through our resources how such agile initiatives have transformed your teams—come share with us your experiences.
FAQs
Agile transformation is a comprehensive shift in organizational processes, culture, and mindset to improve adaptability, collaboration, and customer value delivery.
It enables organizations to respond quickly to market demands, improve innovation, and enhance customer satisfaction while maintaining competitive advantage.
Agile organizations are flexible networks with empowered teams, prioritizing collaboration and customer-centricity, unlike the rigid hierarchies of traditional organizations.
Flexibility, iterative development, customer collaboration, and continuous improvement are key principles for achieving organizational agility.
Leaders can foster agility by acting as facilitators, empowering teams, ensuring transparency, and maintaining alignment with strategic goals.
References
- For an agile transformation, choose the right people. (2021, August 27). https://hbr.org/2021/03/for-an-agile-transformation-choose-the-right-people
- Paasivaara, M., & Lassenius, C. (2016). Challenges and Success Factors for Large-scale Agile Transformations: A Research Proposal and a Pilot Study. Proceedings of the Scientific Workshop Proceedings of XP2016. https://doi.org/10.1145/2962695.2962704.
- Popoola, O., Adama, H., Okeke, C., & Akinoso, A. (2024). CONCEPTUALIZING AGILE DEVELOPMENT IN DIGITAL TRANSFORMATIONS: THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS AND PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS. Engineering Science & Technology Journal. https://doi.org/10.51594/estj.v5i4.1080.
- Helmlinger, P. (2023). Agile Transformation: A Case Study on Early Stage of Agile Adoption. Naše gospodarstvo/Our economy, 69, 56 – 67. https://doi.org/10.2478/ngoe-2023-0006.
- Tshabalala, M., & Marnewick, C. (2021). Agile as an enabler towards innovation-based organisational transformations. SA Journal of Information Management. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajim.v23i1.1309.
- Pacheco, A., Mogrovejo, D., Yupanqui, R., Garay, J., & Uribe-Hernández, Y. (2024). Digital transformation and agile methodologies: An innovative model for competitiveness in the manufacturing sector. Journal of Infrastructure, Policy and Development. https://doi.org/10.24294/jipd.v8i7.4776.
- Putra, I. (2022). Digital Transformation and Agile Leadership: Bibliometrics Analysis and Future Avenue. Journal of International Conference Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.32535/jicp.v5i4.1926.
- Kurakova, C., & Safiullin, N. (2020). IMPLEMENTATION OF AGILE METHODOLOGY IN THE PROCESS OF DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION OF AGRICULTURE. Vestnik of Kazan State Agrarian University. https://doi.org/10.12737/2073-0462-2020-114-120.
- Dragičević, Z., & Bošnjak, S. (2020). Agile Development Process in The Software Factory of the Future. Proceedings of the 25th International Scientific Conference Strategic Management and Decision Support Systems in Strategic Management. https://doi.org/10.46541/978-86-7233-386-2_43.
- Widjaja, P. (2023). Effective Employee Management in Times of Organizational Transformation. Advances in Human Resource Management Research. https://doi.org/10.60079/ahrmr.v1i3.195.
- Daraojimba, E., Nwasike, C., Adegbite, A., Ezeigweneme, C., & Gidiagba, J. (2024). COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW OF AGILE METHODOLOGIES IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT. Computer Science & IT Research Journal. https://doi.org/10.51594/csitrj.v5i1.717.
- Al-Saqqa, S., Sawalha, S., & Abdelnabi, H. (2020). Agile Software Development: Methodologies and Trends. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol., 14, 246-270. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v14i11.13269
- Amajuoyi, P., Benjamin, L., & Adeusi, K. (2024). Agile methodologies: Adapting product management to rapidly changing market conditions. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews. https://doi.org/10.30574/gscarr.2024.19.2.0181.
- Pacheco-Cubillos, D., Boria-Reverter, S., & Gil-Lafuente, J. (2024). Transitioning to Agile Organizational Structures: A Contingency Theory Approach in the Financial Sector. Syst., 12, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12040142.
- Gustavsson, T., Berntzen, M., & Stray, V. (2022). Changes to team autonomy in large-scale software development: a multiple case study of Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) implementations. International Journal of Information Systems and Project Management. https://doi.org/10.12821/ijispm100102.
- Manubrahma, S., Shireesha, S., & Varalakshmi, T. (2024). Effect of Change Management Strategies on Organizational Transformation. International Research Journal on Advanced Engineering and Management (IRJAEM). https://doi.org/10.47392/irjaem.2024.0215.
- Gren, L., & Lenberg, P. (2019). Agility is responsiveness to change: An essential definition. Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1145/3383219.3383265.
- Brosseau, D., Ebrahim, S., Handscomb, C., & Thaker, S. (2019, May 10). The journey to an agile organization. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our-insights/the-journey-to-an-agile-organization#/
- Zack, T. (2023, November 10). Agile Transformation: The Guide to Getting started. LeadingAgile. https://www.leadingagile.com/2018/07/the-basics-of-agile-transformation/
- De Smet, A., Lurie, M., & St George, A. (2018, October 1). Leading agile transformation: The new capabilities leaders need to build 21st-century organizations. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our-insights/leading-agile-transformation-the-new-capabilities-leaders-need-to-build-21st-century-organizations
- Maule, K. (2024, November 15). Agile Transformation: 11 Keys to success. Wellingtone. https://wellingtone.co.uk/keys-to-success-agile-transformations/
- Moustafa, A., & Abdulrasoul, M. (2024). Factors Affecting the Success of Agile Software Teams. International Journal of Computers and Informatics. https://doi.org/10.59992/ijci.2024.v3n2p1.
- Sandstø, R., & Reme-Ness, C. (2021). Agile Practices and Impacts on Project Success. Journal of Engineering, Project, and Production Management, 11, 255 – 262. https://doi.org/10.2478/jeppm-2021-0024
- Mardian, M. (2024). Determinant of Agile Leadership: A Systematic Literature Review. KnE Social Sciences. https://doi.org/10.18502/kss.v9i11.15836.
