Jump to the section
Key Learnings
#1
Prioritize Effectively
Identify your most important tasks and focus on them. By concentrating on high-priority activities, you ensure that your efforts align with your goals.
#2
Set Clear Goals
Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Clear objectives provide direction and motivation, helping you stay on track.
#3
Develop Self-Discipline
Stay committed to your tasks and goals, even when faced with distractions or challenges. Self-discipline is key to maintaining consistent progress.
#4
Reflect and Adjust
Regularly assess your progress and adjust your strategies. Reflection allows you to learn from experiences and continuously improve your self-management skills.

Have you ever felt that you are at a plateau despite your efforts in developing your skills? Have you ever been frustrated by just spinning your wheels on the path to personal growth and effective leadership? You set ambitious goals, deep dive into self-help books, and attend masterclasses or workshops, but still, something is missing. What if this missing piece of the puzzle is mastering yourself? What is missing the most important part of emotional intelligence for leaders, such as self-management, self-discipline, and self-control? It is an essential part of your personal development journey.
This article will guide you into a transformative journey to discover what it truly means to manage yourself. We will dive deep into aligning emotions, behaviors, and decisions with long-term goals and aspirations. This can revolutionize not only your leadership capabilities but also your personal growth. Getting insights from leaders such as John Maxwell and Daniel Goleman, we will explore practical strategies and tips for developing your self-management skills. If you want to make the next step in your personal development and unlock your full potential you are in the right place. Your path to mastering self-management and becoming a leader with purpose and confidence can start here.
Why Self-Management is important?
Self-management is at the center of effective leadership and an essential part of your emotional intelligence. As John Maxwell states in “The 5 Levels of Leadership” book, leadership is not only a title but a continuous process of growth. This means that you have to develop multiple skills and behaviors to become an effective leader. In leadership, self-discipline and self-control are important skills for helping you navigate through challenges, and influence and inspire others for success. Leaders who master self-management, not only lead by example but also create an environment where teams can thrive. Self-management is not only about organizing your tasks and checklist, it is about understanding and managing your emotions, behaviors, and decisions for achieving long-term goals.
Leadership Challenges
In the last decade, leadership has transformed significantly. After Covid-19 the rise of remote and hybrid teams came into focus. In this setting, leaders face new challenges in maintaining engagement, communication, and building trust in their teams. The physical distance in remote work environments creates barriers to building strong relationships. Leaders must adapt their strategies and how they respond to challenges to ensure that the team remains productive and motivated.
Globalization has also influenced the way leadership operates. Leaders today must operate in diverse teams across different cultures, setting expectations and adapting to multiple working styles. This requires that the leaders develop a high degree of cultural intelligence. Leaders must be able to communicate effectively, showing empathy and understanding toward individuals and various cultural backgrounds. Emotional Intelligence, according to Goleman (2015), is the most important part is such leadership dynamics. Leaders who can adjust their styles, adapt their methods, and understand cultural differences are more effective and less frustrated.
Leading Diverse Teams
As globalization continues to drive the business landscape, leading diverse teams is an important element of successful teams and leadership. Diversity in the team brings multiple perspectives and skills together. This enables teams to solve complex problems, become creative, and make better decisions. For effective use of team diversity, leaders must actively promote inclusion and diversity. In “The Leadership Challenge: How to Make Extraordinary Things Happen in Organizations”, Kouzes and Posner (2017) argue that leaders who build an inclusive environment, encourage different team members to contribute their unique contributions. This leads to an innovative and effective outcome, as well as better team engagement.
In that way, you have to develop your cultural intelligence, as the ability to understand the adapt to different cultural contexts. This is an important skill for mastering self-management. A leader who understands different cultural nuances can comprehend better how different cultures respond. This can ensure a cohesive and respectful team dynamic, where all members feel valued and engaged.
Adapting to Business Changes
As technology is changing almost every day and organizations are evolving continuously, leaders must become more agile. The ability to adapt to new technologies, trends, and shifting business models is important for a leader to stay competitive. Agile leadership is defined by the ability of the leaders to be flexible, with a growth mindset, and willing to embrace change. In “Leadership: Theory and Practice”, Northouse (2021), emphasizes that leaders who embrace continuous learning can adapt better to changes and lead their teams better through change management and transitions.
Technology plays an important role in modern leadership. Leaders must not only adopt new technological tools and platforms, such as Artificial Intelligence but also integrate them into their strategies. This enhances collaboration and team productivity. Leaders must remain alert to changes, but they need also to balance the human element and technology usage. They must ensure that technology and tools do not diminish personal connection and relationships in the team.
Balancing Professional and Personal Growth
The concept of “work-life integration” has become more relevant for leaders’ well-being and effectiveness. Instead of striving for the perfect work-life balance between personal and professional responsibilities, leaders must learn to integrate both worlds to optimize their well-being and respect their values. In “Mastering Self-Leadership: Empowering Yourself for Personal Excellence”, Neck and Manz (2010) emphasize that leaders who manage stress and maintain personal well-being are essential for long-term leadership success. Leaders who manage their time effectively, prioritize self-care, and align their values with their professional goals are more likely to lead with clarity and purpose.
Self-reflection and mindfulness play an important role in achieving work-life integration. Leaders must regularly evaluate how their personal and professional worlds intersect and evolve. They need to adjust both personal and professional priorities and not sacrifice one or the other. They need to monitor their needs and the needs of others for re-assessing their focus for better work-life integration. This process allows them to stay focused on their goals while maintaining their energy and resilience for navigating challenges in private and professional domains.
Aligning Personal Values with Organizational Goals
To be effective in leadership, leaders must be authentic. Leaders who align their values with their organization’s goals are more likely to be effective and inspire loyalty and commitment in their teams. According to “What Makes a Leader?” Goleman (2015) highlights authentic leadership, as the role of a leader to lead with integrity and respect values. This builds trust and fosters a positive organizational culture. Ethical decision-making aligns with the authentic leadership concept, as the leader is always acting according to the values and leads by example in their teams.
Self-Management Definition
Self-management is crucial for leadership and personal development towards success. A leader can regulate emotions, thoughts, and behaviors, especially during challenges and stressful situations. Leaders who master self-management lead with clarity, focus, and consistency. Leaders without self-management react impulsively, losing credibility and their trust in their teams. But let’s see what it makes for a leader to master self-management.
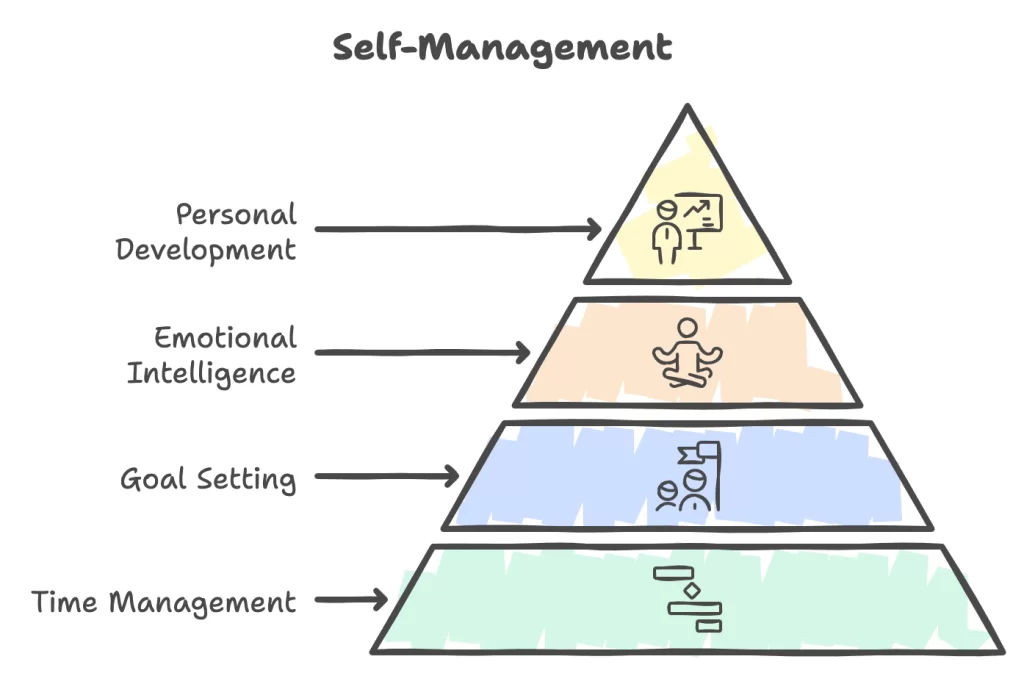
By definition, self-management is the ability to regulate yourself, emotions, and reactions in various situations. This includes managing your time, setting goals, and developing emotional intelligence. In “Lead Yourself Before You Lead Others” by Franklin Covey (2023), it is emphasized that leadership starts with yourself. Before leading others, leaders must understand and manage themselves. This is why self-management is considered the basis for effective leadership.
Time Management
One of the most practical aspects of self-management is time management. Modern leaders are juggling multiple tasks and responsibilities at the same time, both in personal and professional settings. Managing one’s self effectively means prioritizing tasks to maximize productivity, creating and adhering to schedules, and also maintaining a healthy integration of personal and professional life. This integration is essential for well-being and preventing burnout. Based on Asana’s “What is self-management? (7 skills to improve it)” leaders who master time management not only improve their productivity but also set an example for their teams.
Goal Setting
Self-management involves also setting clear and achievable objectives. Effective leaders reflect on their capabilities and capacity break down goals into actionable steps and evaluate regularly their strategies and progress. This process of goal setting ensures that leaders evaluate their progress and assess obstacles and challenges. A structured approach to goal setting empowers leaders to align goals and actions with the broader vision. This contributes to both personal development and organizational success.
Emotional Intelligence
There is no self-management without proper skills in emotional intelligence. Leaders with high emotional intelligence can understand and manage their emotions. They can recognize their emotional triggers and manage their emotional state. This allows them to develop coping mechanisms and strategies during challenging situations. Emotional intelligence and self-awareness equip leaders to maintain composure in conflicts and navigate better interpersonal dynamics. It also plays a pivotal role in decision-making, as managing emotions effectively is more likely for leaders to make better and more thorough informed decisions.
Impact on Personal Development
Self-management is crucial for personal growth and development. It encourages the habit of life-long learning and continuous improvement. This allows for individuals to remain adaptable and resilient in the face of adversity. Leaders who are committed to managing themselves align their actions with their values and goals. This fosters both personal and professional growth. According to “The Benefits of Self-Control and Discipline” from Positive Psychology (2023), self-discipline helps individuals achieve greater satisfaction in their personal lives. It can also promote a consistent alignment between their goals and daily actions.
What is Self-Discipline?
Self-discipline is the ability to control one’s actions, thoughts, and emotions in the process of achieving long-term goals, even if there are temptations, distractions, or obstacles. It is the consistent commitment to personal and professional goals. It is not about resisting temptations but making thoughtful, intentional choices to overcome these temptations by choice. Then one can cultivate perseverance, habits, and resilience to achieve success. For this reason, self-discipline is an important skill for leaders who have ambitious and long-term goals for themselves and their teams.
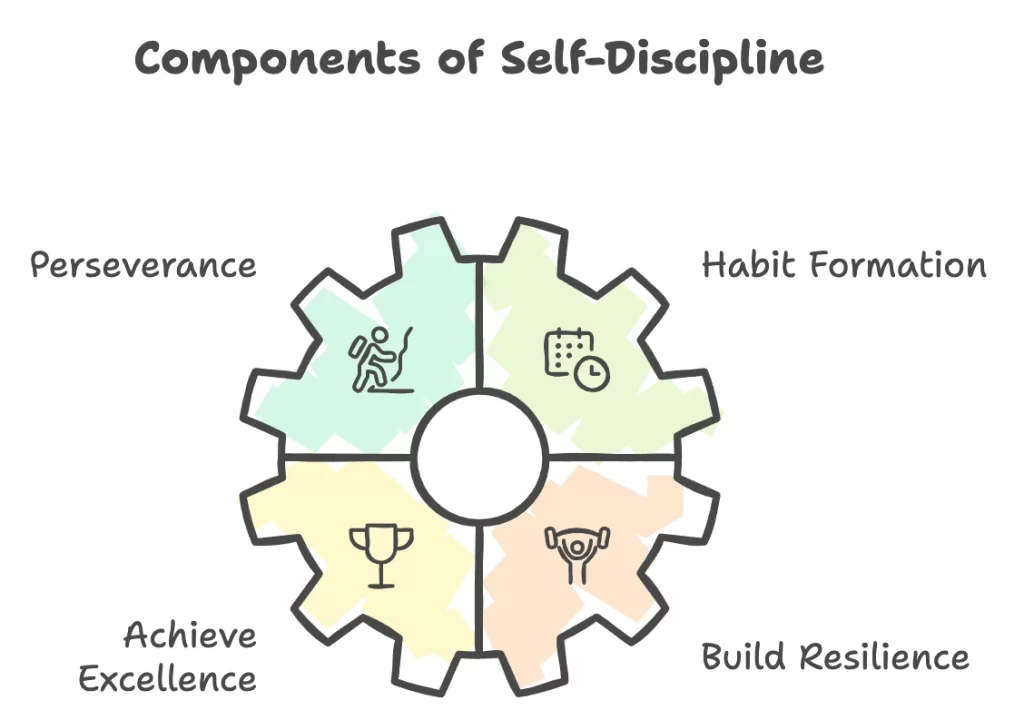
Perseverance
The main characteristic of self-discipline is perseverance. Leaders and individuals with strong self-discipline can stay focused and motivated, even in case of obstacles and setbacks. With perseverance, they stay committed to their long-term goals which helps them push through discomfort and distractions. With self-discipline, the leader is focusing on the end goal, knowing that setbacks are short-term and temporary.
Habit Formation
Another aspect of self-discipline is its role in habit formation. Success is achieved by establishing positive habits that align with personal and professional goals. Using self-discipline for repeating a routine a new habit can be formed and established. In that way, a leader can turn intentions into consistent action over time. By cultivating habits such as regular exercise, reading, or skill development, leaders can ensure that they are moving toward their personal and professional goals.
Achieve Excellence
The leaders who embrace self-discipline often strive for excellence. They hold high standards and consistently work to improve themselves. This commitment to growth and excellence does not benefit only the leaders but also sets a powerful example for their teams. Such leaders inspire others to push beyond their limits. Discipline is not only about personal success, it is about driving a culture of resilience and accountability within teams. When leaders demonstrate a consistent commitment to high performance, they foster an environment where others feel motivated to meet these standards.
Build Resilience
Through perseverance, strong habit formation, and striving for excellence, the next benefit of self-discipline is the building of resilience. Leaders with self-discipline can view challenges with determination for solving and opportunities for learning. This mindset allows them to persevere when faced with adversity, adapt to circumstances, and learn from their experiences. Therefore the ability to overcome obstacles is a strong trait of effective leadership. Leaders can remain composed and focused, even to the highest challenge, allowing them to guide their team during difficult times.
Exploring Self-Control
Self-control is the ability to regulate one’s impulses, emotions, and desires, particularly in challenging situations. Leaders who possess strong self-control can better navigate themselves in complex environments with a lot of unknowns. They can maintain their professionalism, and make rational decisions even under stressful situations. This in turn impacts their teams and organizations.

Maintaining Professionalism
As mentioned, leaders with high self-control can keep their composure even under extremely stressful situations. This can inspire others to remain calm and navigate the team to make better decisions. During a crisis, when a leader is calm, it can provide stability and guidance to her team. Based on “The Importance of Self-Control” in Working Capital Review (2017), this consistency in behavior fosters a culture of reliability and professionalism within the organization.
Making Rational Decisions
Leaders with strong self-control can avoid making reactions to critical situations based on emotions. They pause and reflect before they decide and act. They can consider the long-term consequences of their decisions and lead to more thoughtful decisions. This ability to resist impulsive decisions and reactions often results to better outcomes for both individuals and organizations.
Managing Stress
Leaders and their teams facing high-pressure situations can lead to high stress and conflicts. Leaders with self-control can better manage these stressful situations and remain calm and effective. Through mindfulness and determination can engage in self-care techniques and manage their stress effectively. In that way, leaders can maintain their overall well-being and remain focused on their duties and responsibilities.
Impact on Relationships
Based on all the above benefits of self-control, such leaders can build strong personal and professional relationships. Such leaders can build trust, even in challenging situations and high-conflict environments. They exhibit patience and understanding, leaders can resolve conflict with productive discussions and connections with their teams. This ability contributes to improving their relationships by helping others cope with stress and conflicts.
Practical Strategies for Self-Management
Effective self-management involves also the development of strategies and habits that enable individuals to apply them in practice. These techniques and habits can help them regulate their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, ensuring they are aligned with both their goals and values. Hereafter we provide some effective strategies to develop self-management in your everyday life.
Strategy#1: Practice Self-Reflection and Mindfulness
Mindfulness practice is a powerful tool that enables you to become more attuned to your thoughts and emotions. Practicing mindfulness helps you to improve your emotional intelligence, making you more effective in managing challenging situations. By regularly engaging in self-reflection, leaders can gain valuable insights into their thoughts and emotions. This provides the chance to reflect, manage stress, and identify areas for improvement.

Regular mindfulness practice can support assessing your thoughts and feelings, which allows for clearer decision-making and reduces emotional reactivity during stressful situations. Self-reflection allows for assessing your progress against personal and professional goals. This process ensures the monitoring of the progress of your goals and also the alignment of your actions and thoughts with your values. Mindfulness strategies, as stated in “Mindfulness: Strategies to implement targeted self-care” from NCBI, play an important role in promoting emotional regulation and self-care, and both are essential for effective leadership.
Strategy#2: Align Your Values with SMART Goals
One important aspect of practicing self-management is to align your values with your personal and professional goals. When your values support your objectives, you are in harmony and motivated to achieve your goals. The first step is to reflect on your core values and beliefs and then integrate them into your goal-setting process.
Reflection on your values and beliefs is an important element for your self-management development path. You have to identify what truly matters to you both personally and professionally. Then the next step is to set value-driven goals. You have to ensure that the goals you set are in harmony with your core beliefs. For example, if your value is creativity and curiousness, then you have to set goals that meet with creating new and learning during your objective achievement. Aligning your values with your goals fosters your motivation for long-term fulfillment.
Then the next step is to set SMART goals. As SMART goals we define the objectives that are: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bounded. By setting SMART goals, you create a structured approach for your development. This increases your clarity and focus in the process of achieving such objectives. In that way, you can break, long-term ambitions into manageable and achievable tasks. This makes you believe in these objectives and also measure progress and success. Some examples can be found in “SMART (SMART goals)” from TechTarget.
Strategy#3: Review regularly and adjust your Goals
Setting goals is an important event that puts clarity and focus. But it is not enough, especially in the long-term goals. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your goals is key to mastering self-management. This approach allows you to stay flexible and adapt to dynamic situations.
First, you have to monitor progress, by scheduling regular check-ins to evaluate how well you are advancing towards your goals. Then you have to asses if adjustment is needed. If your objectives are becoming irrelevant or unattainable, then you have to modify them even if to change them. Your goal here is to review and adapt to remain relevant and efficient for the achievement of your goals.
Strategy#4: Master time management techniques
Effective time management is crucial for self-management in leadership. Using management tools, such as planners, boards, and project management, leaders can efficiently organize their tasks and set priorities. Time management ensures that the priorities and expectations for tasks are met while maintaining a healthy balance between personal and professional responsibilities. Setting clear priorities helps to focus and reduce stress levels, which prevent burnout. This is important for maintaining long-term effectiveness in leadership roles.

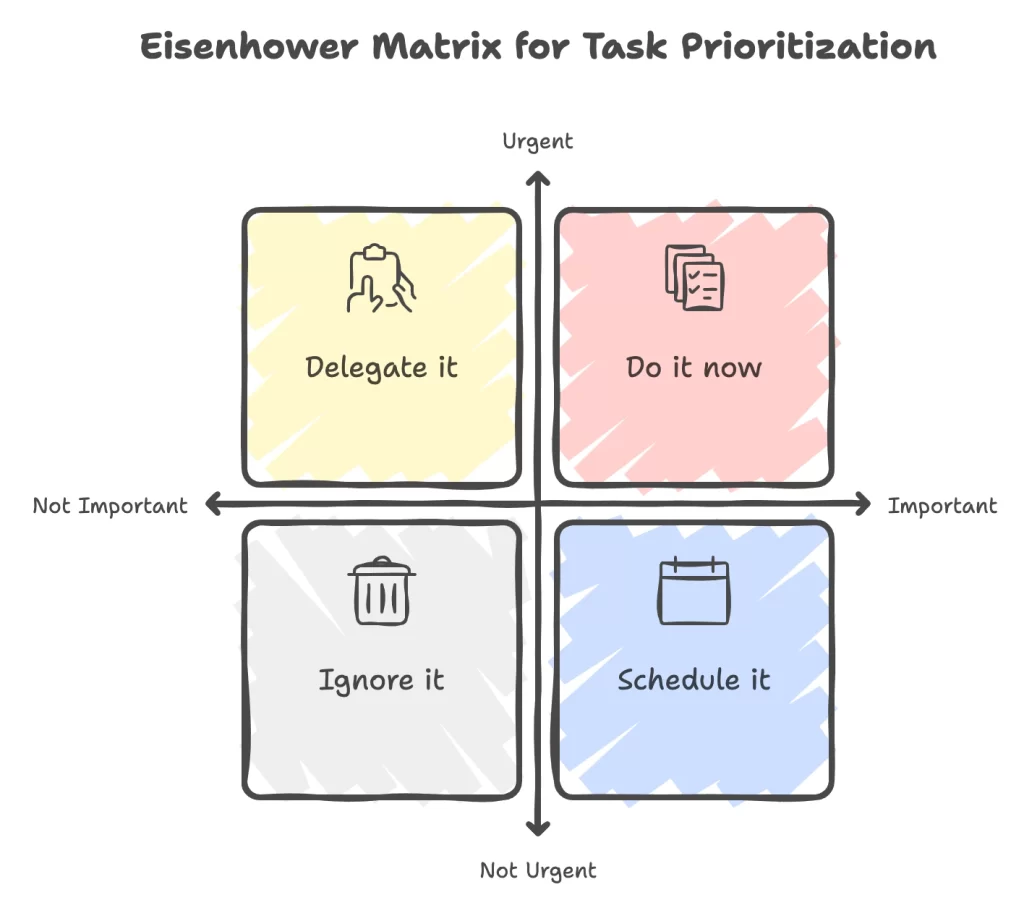
Prioritization Tools
One of the most effective prioritization tools is the Eisenhower Matrix. You can categorize your tasks to important/urgent, important/not-urgent, not-important/urgent, and not-important/not urgent:
- Important and Urgent: Do it now. Set clear deadlines and a plan to do the task
- Important and Not-Urgent: Schedule it. Set a plan but not a clear deadline.
- Not-Important and Urgent: Delegate it. Provide clear guidelines and give them to other people to perform the task.
- Not-Important and Not-Urgent: Ignore it. Do not proceed as this makes no progress towards your goals
For visualization of tasks and priorities, you can use project management and scheduling tools, such as Trello, Asana, or MS Project. With such tools, you can organize your tasks, set priorities collaborate with other people, and maintain accountability.
Minimizing Distractions
Distractions can be detrimental to your time management and your organization of tasks and priorities. It maximizes productivity and self-management it is important to create the right environment that supports you to focus and achieve your goals.
Use a dedicated workspace with minimum interruptions and distractions. This means using quiet space or even noise-canceling headphones if you work in a collaborative working space. It important is also to set your digital environment to minimize distractions, such as avoiding automatic notifications and setting “do not disturb” messages to collaboration tools. Setting the environment for focus is important for maximizing your efficiency and maintaining your self-management of tasks and emotions.
Time-blocking techniques are also important for setting out time and space to think and make productive work. Pomodoro Method is the most famous, for setting periods of focused work with short breaks. This can help you to maintain your concentration and improve your productivity. By achieving these time-blocking slots, you can keep your stress levels down and improve your satisfaction and self-management.
Develop a Secret Tool for Personal Growth
Mastering self-management, self-discipline, and self-control are important achievements in personal and professional life. They are the fundamentals for effective leadership and improving your emotional intelligence. Imagine that you need to sail a boat without navigation. You are at the mercy of the wind and tides. In that way, if you do not have your internal navigation for personal development and leadership skills, you feel like sailing to an unknown destination or making loops.
By developing self-mastery you interconnect all these skills and qualities. You are not implementing a checklist, but you are aligning your actions, decisions, and emotions with your long-term objectives and personal values. This alignment provides you with the motivation to persevere in any situation and environment. It sets you up for managing your emotions and your actions through self-management and self-control.
We are calling you to reflect on these insights and invest time to develop these essential skills. You have to set clear goals, manage your time wisely, and cultivate the habits to support your journey. You have to remember that personal development is not a sprint but a marathon. It is about taking consistent, intentional steps towards your long-term goals. Your secret solution to that is to develop your self-management skills, which provide discipline and self-control toward mastery. Your future self, your family, and your team will benefit from your authentic leadership and self-management skills.
FAQs
Self-management in leadership is the ability to control one’s emotions, behaviors, and time to effectively lead others and achieve goals.
Self-discipline promotes consistent actions toward personal goals, fostering growth and the establishment of positive habits.
Self-control is managing impulses and emotions. It’s vital for making rational decisions and maintaining professionalism.
Managing oneself ensures that leaders act as role models, make sound decisions, and inspire trust and confidence in their teams.
Strategies include setting clear goals, practicing mindfulness, developing routines, and reflecting on personal progress.
